
In operating systems based on the Linux kernel, various package managers are used, allowing you to download and install available programs. In addition, there are individual packages where applications are already stored. They only need to run through a specific tool so that it is unpacking and compiling, after which it will be available for use. Today we would like to affect the installation topic on the example of the most popular distributions, tell us in detail about each accessible installation option and show in practice how it all works.
Install programs in Linux
Of course, at the moment there is a huge number of the most diverse distributions, but a certain part of them is based on existing platforms and has the same bones, but with the addition of some of its functions from the developers. Next, we will touch on the topic of three popular branches, where the installation operation is different, and you, based on the information provided, can already find information that is suitable for the distribution used.
As you can see, the APT is quite implemented. It is also worth considering that in the latest version of Ubuntu to write, APT-GET is completely optional, you can shorten simply to the APT, and already enter Install. Here are some examples of popular applications that are available for installation through official storage facilities:
Sudo Apt Install VLC - video player.
Sudo Apt Install Gnome-Music - Music Player.
Sudo Apt Install Gimp - graphic editor.
Sudo Apt Install Gparted - on the control of the hard disk partitions.
Redhat, Centos and Fedora
In distributions, where the RedHat platform is taken as the basis, Yum is the main manager. It works by analogy with the already considered tool, only here is controlled by RPM format directories. Installation of software from official repository is practically no different and looks like this:
- Run the console by any convenient method.
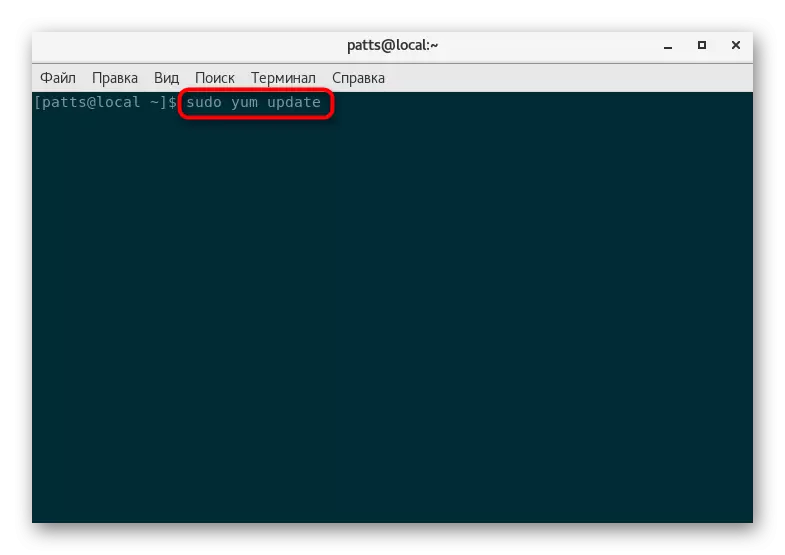
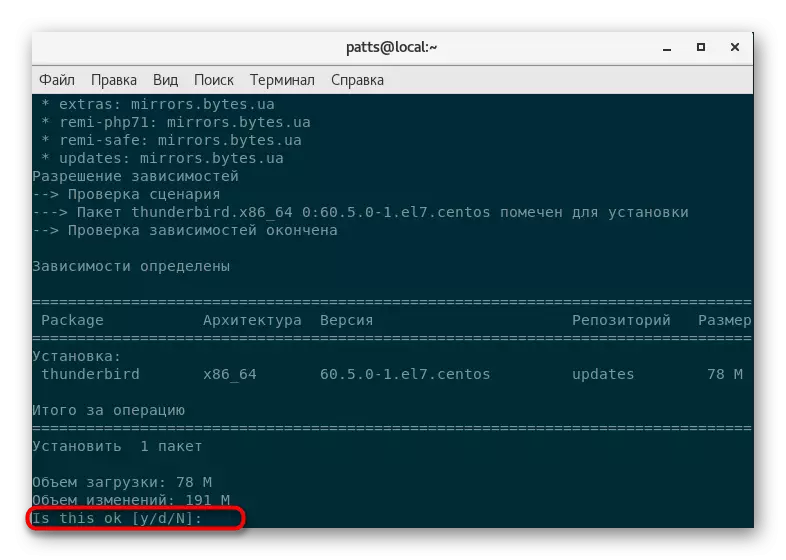
- Update a list of system repository through Sudo Yum Update.
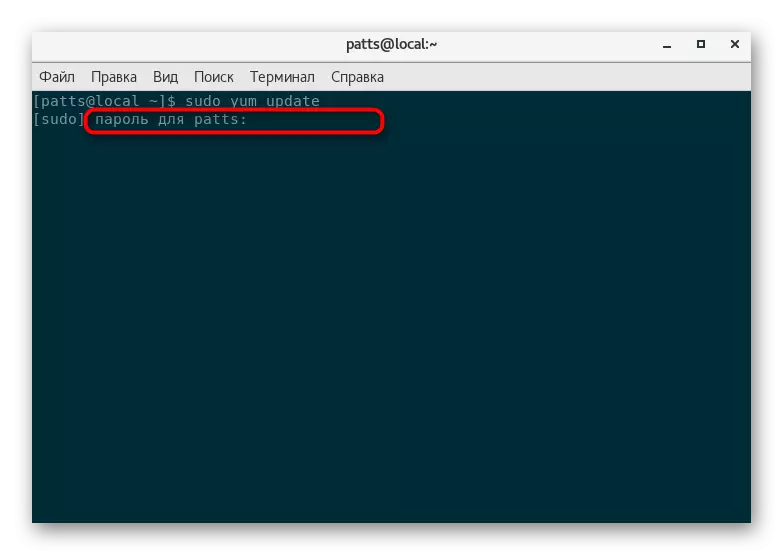
- Confirm the action by entering the root access password.
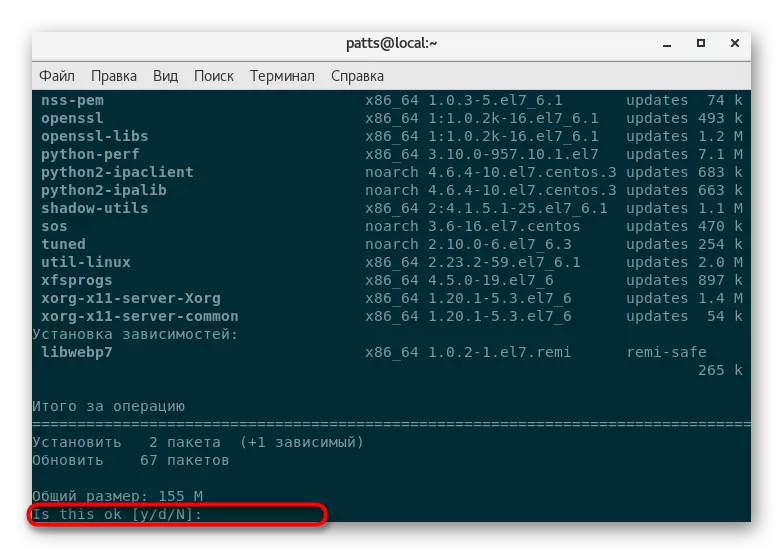
- Take an agreement with the addition of new files by specifying the Y version.
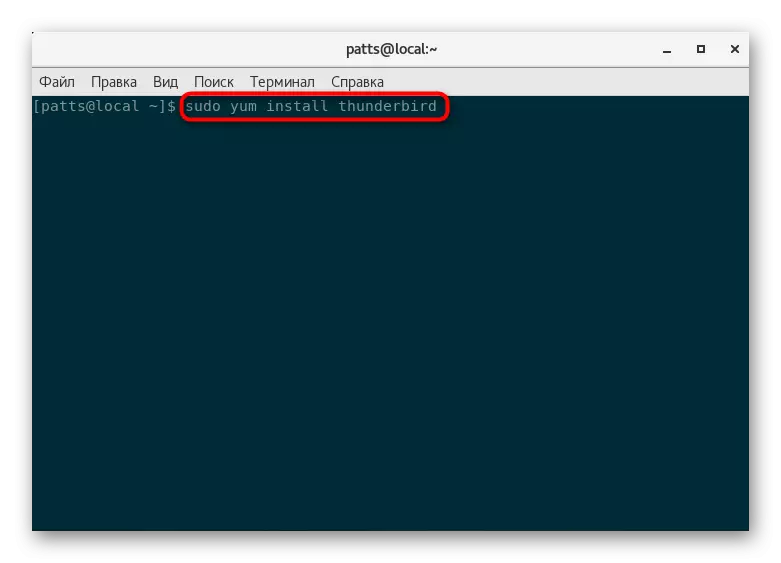
- At the end of the update, sudo yum Install Thunderbird and activate it. For example, we took the Thunderbird email client, you can replace the last expression in the row to any other necessary software.
- Here you will also need to specify an option Y to download.
- Expect the download and unpacking the application components.

By analogy with the previous package manager, let's give several examples of using YUM to install certain programs:
Sudo Yum Install Java - Java components.
Sudo Yum Install Chromium - Browser Chromium.
Sudo Yum Install Gparted - drives management program.
Arch Linux, Chakra, Manjaro
It remains to consider the last third branch of distributions, which was taken by Arch Linux. Here is the Pacman manager. It works with TAR formats packages, and loading components is made through specially designated sites using FTP or HTTP protocols. We have taken for an example of the Manjaro distribution with a standard graphical interface and want to visually demonstrate the procedure for using PACMAN.
- Open the graphic shell menu and go to work in the classic console.
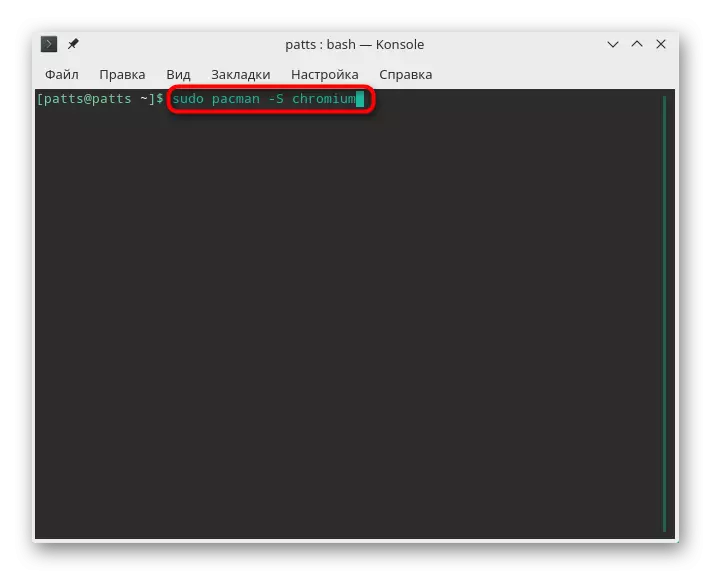
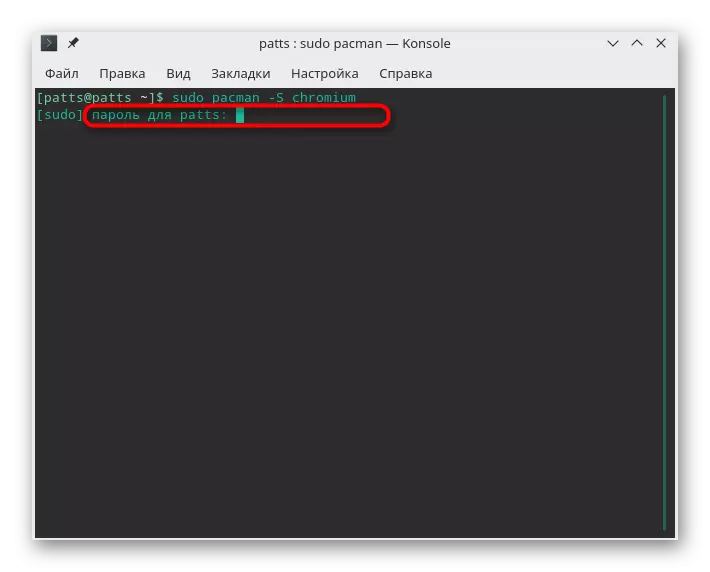
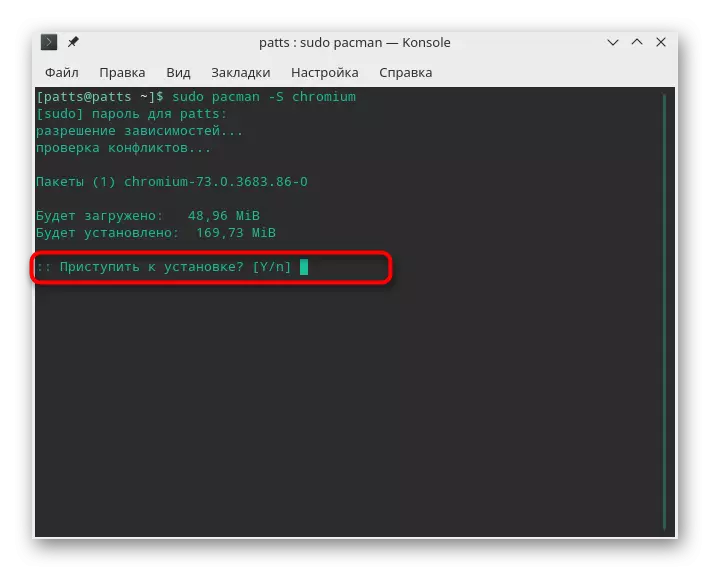
- Install, for example, a popular chromium browser. To do this, enter Sudo Pacman -S Chromium. Argument -s is just responsible for the fact that the command must be downloaded and installing the program.
- Confirm the authenticity of the superuser account by entering the password.
- Take the installation of components by selecting the Y version.
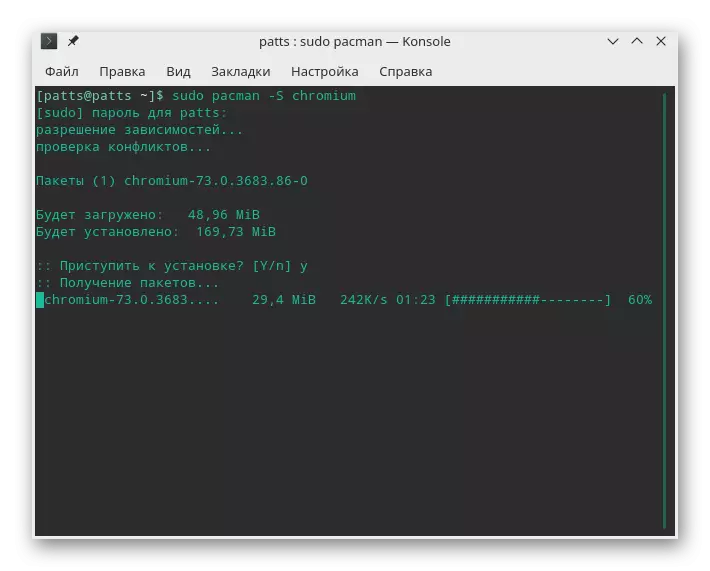
- Expect downloads: To successfully execute this procedure, you will need to connect to the Internet.
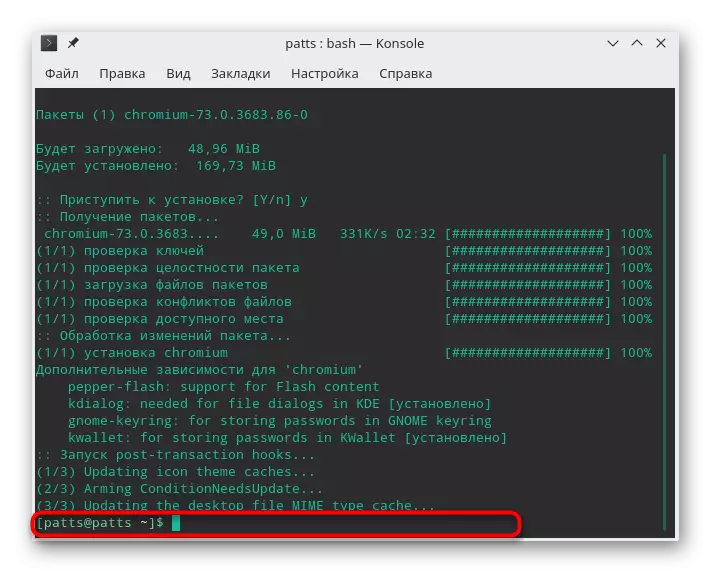
- If a new input line appeared in the console, then the installation has passed successfully and you can go to work in the application.
Examples of adding another popular software look like this:
Sudo Pacman -s Firefox
Sudo Pacman -s Gimp
Sudo Pacman -S VLC
Now you know how the software is installed on three different Linux platforms using official storage through the built-in manager. We want to pay attention to that due to the wrong entry of the installation package on the screen, in most cases a hint appears with the correct option, then it is enough to rewrite the command by correcting the error.
Method 2: Package Manager and Custom Storage
In addition to official repositories of different applications, there are also user. Such an option would be the best solution for those users who wish to obtain a specific version of an application or set them in the order of a few pieces on the computer. This installation method is slightly different and it is considered more difficult, so we offer a detailed look into the matter. If you do not have the address of the repository, you must first find him. The easiest way to do this through a dedicated website, and the whole procedure looks like this:
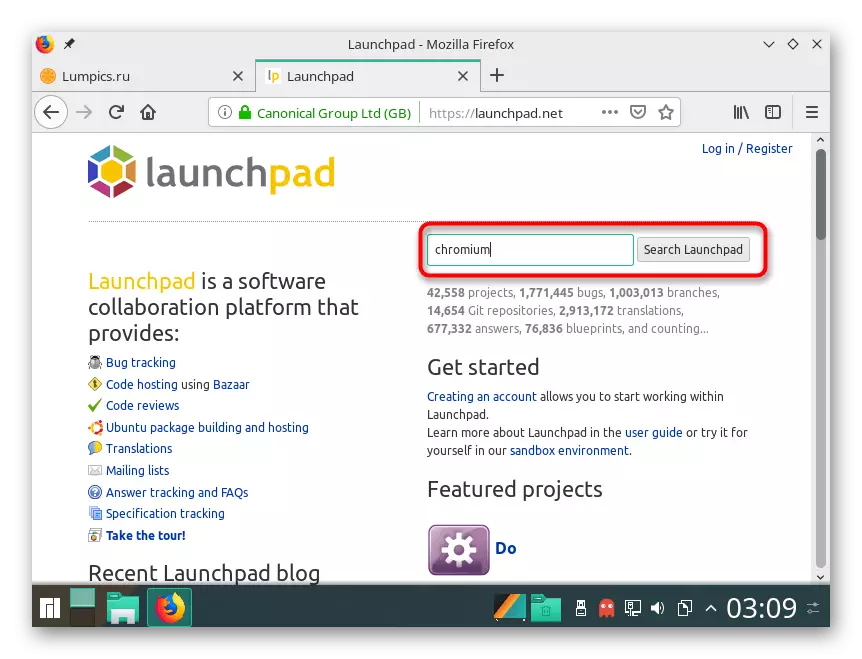
Go to the official website Launchpad
- Click on the above link to the home page and in the search for Launchpad, type the name of the software. For convenience, we can add this line another PPA, which means that the user store.
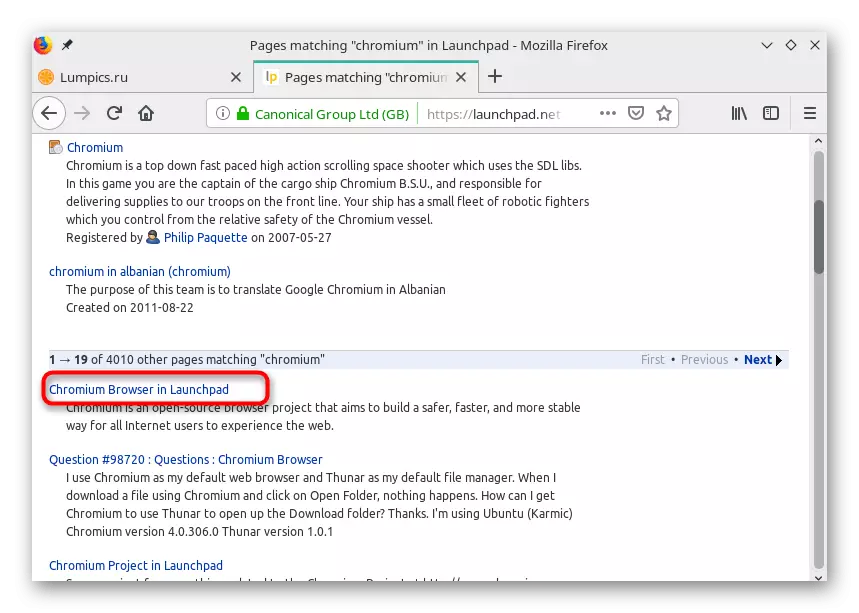
- The results look for the appropriate option and click on the proper link.
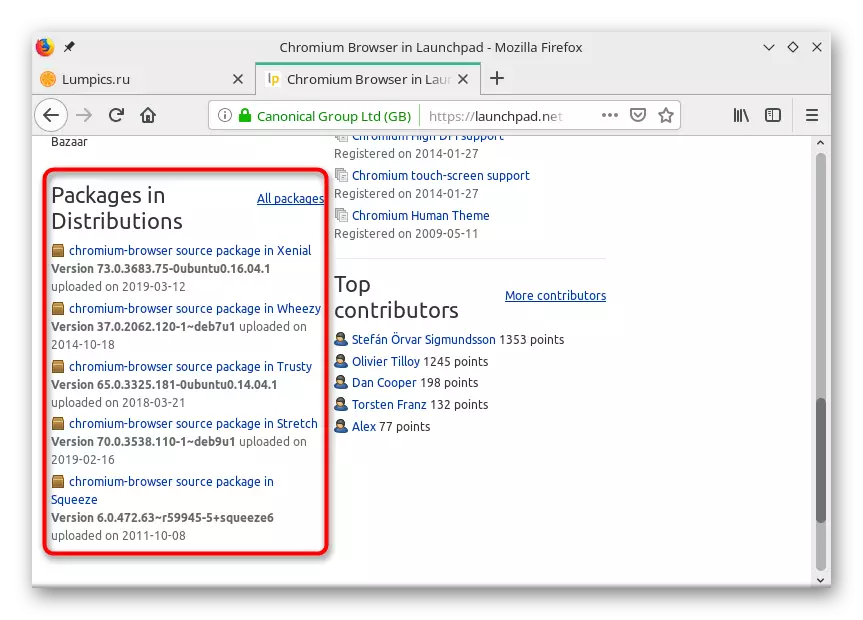
- Check out the possibilities of the package and select the appropriate.
- Go to the software.
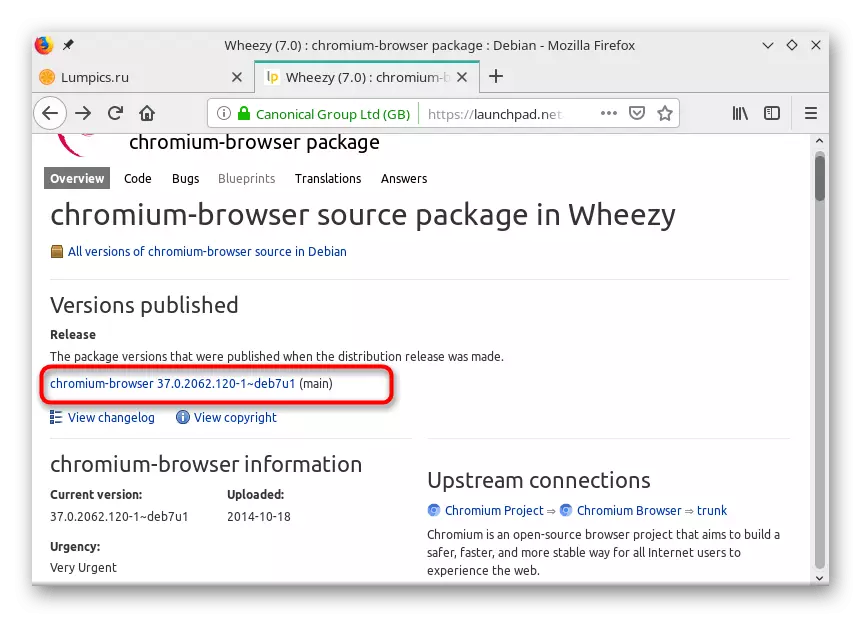
- Once on the PPA page, at the bottom you will see a team with which produced and installation.
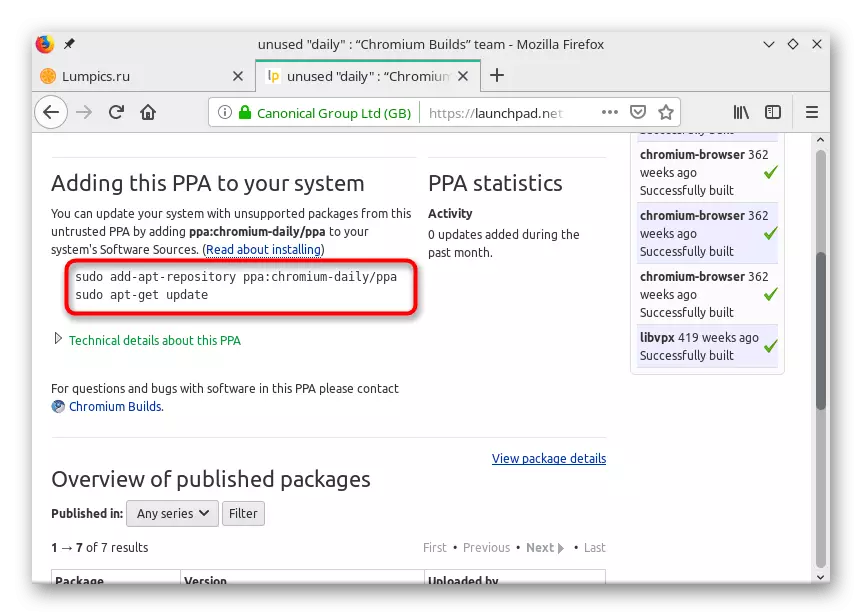
Now that you know about the most popular method of getting links on custom software repositories required versions. It remains only to deal with the intricacies of installing them in different distributions. Let's start all over from the beginning.
Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint
You are already familiar with the standard package manager, which is installed on these platforms. Viewed way to install software also implies the use of this tool, but a preliminary implementation of additional actions. We have already dismantled the example of the addition of Chromium in, now let's take a look at how this is done through a user repository.
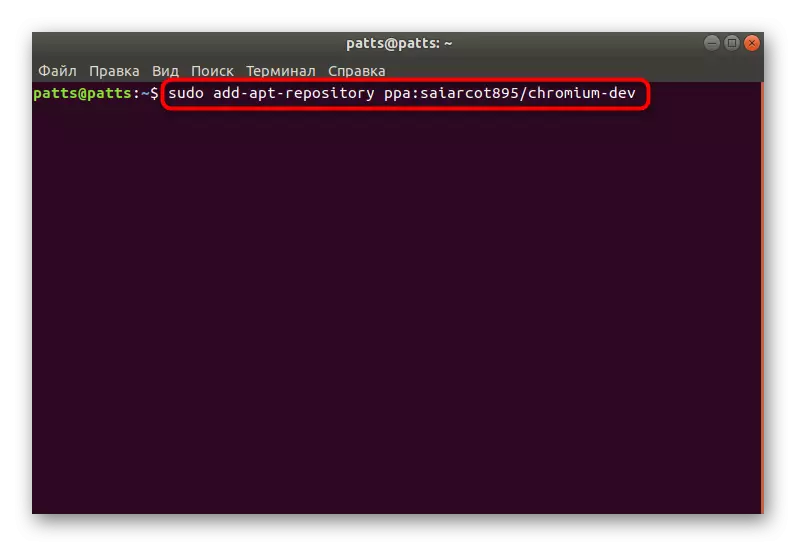
- Locate on the above website link to the repository, and then run the console and put it in there. We will take for example the latest version of the Web browser. sudo add-apt-repository ppa: saiarcot895 / chromium-dev.
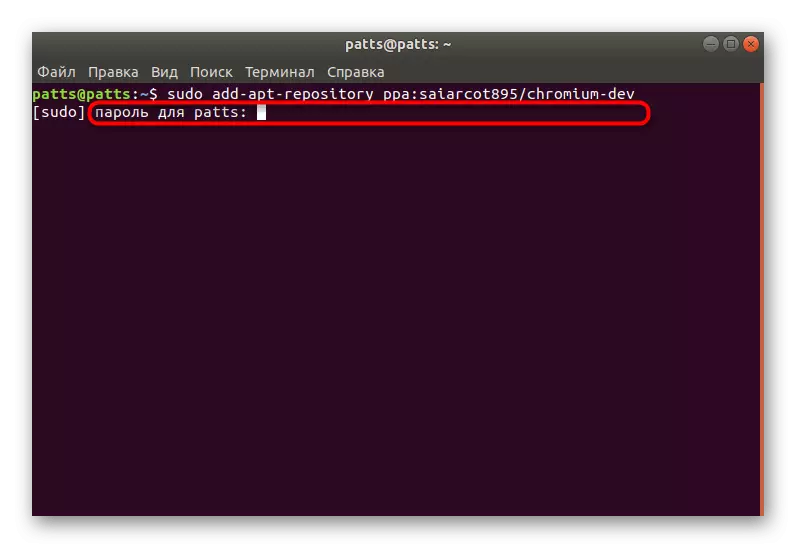
- Confirm the action by entering a password.
- Next, read the list of packages that will be included in the system, and then press the Enter key.
- After the procedure, update the system libraries: sudo apt-get update.
- Use the familiar command to install the browser from the added repository sudo apt install chromium-browser.
- Take the addition of new components, selecting the option D.
- After installation, look in the application menu. There shall be added a new icon, and through which the browser start-up is carried out.

As you can see, nothing complicated in the use of storage facilities there. We just need to find a suitable version of the software on the above site and paste commands given there in the console. After adding the directory will only make the installation of the new version of the familiar one - through apt install.
RedHat, CentOS and Fedora
For these operating systems, make better use of storage and http://mirror.lihnidos.org http://li.nux.ro, there you will find more appropriate directories RPM formats, with regard to their installation directly from the console, without downloading from the site, it is performed in several steps:
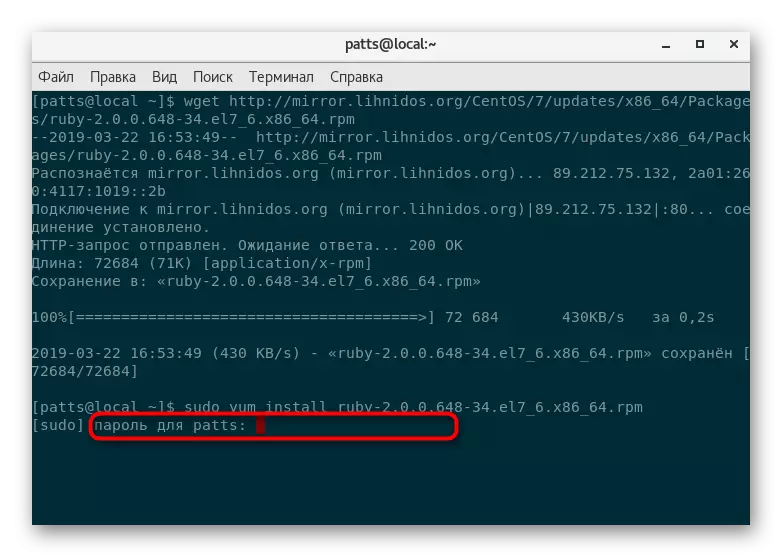
- For example I would like to take the Ruby programming language components. First on the site you need to find a suitable package, and then in the console to enter such an address about wget http://mirror.lihnidos.org/CentOS/7/updates/x86_64/Packages/ruby-2.0.0.648-34.el7_6.x86_64. rpm. Link will vary depending on what kind of repository you are using. After entering the activate command.
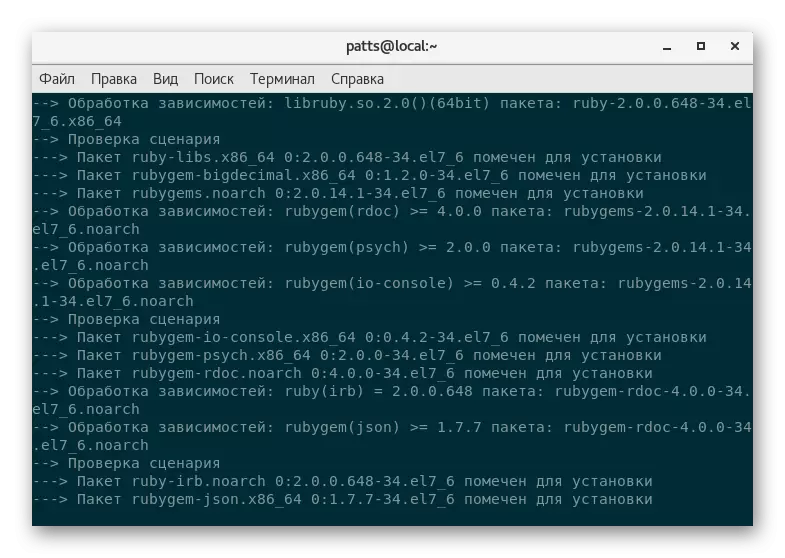
- Next to the computer will be downloaded package will only install it the usual way, so enter sudo yum install + name_package.
- Enable Root Access by entering the password from the main account.
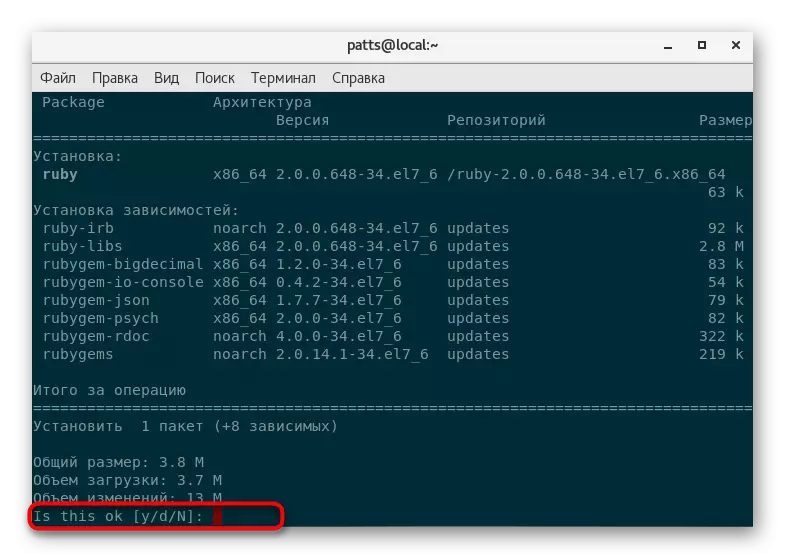
- Expect to complete the test scenarios and compatibility.
- Confirm the setting by selecting a suitable option.

Arch, Chakra, Manjaro
Most stores user repositories for Arch Linux keeps the only file format TAR.GZ, and the method of installation, the system is a little different. It is worth noting that all of the necessary directories can be found on the site aur.archlinux.org. To access this storage on a computer-controlled Manjaro need to first run sudo pacman -S base-devel yaourt - so add additional components.
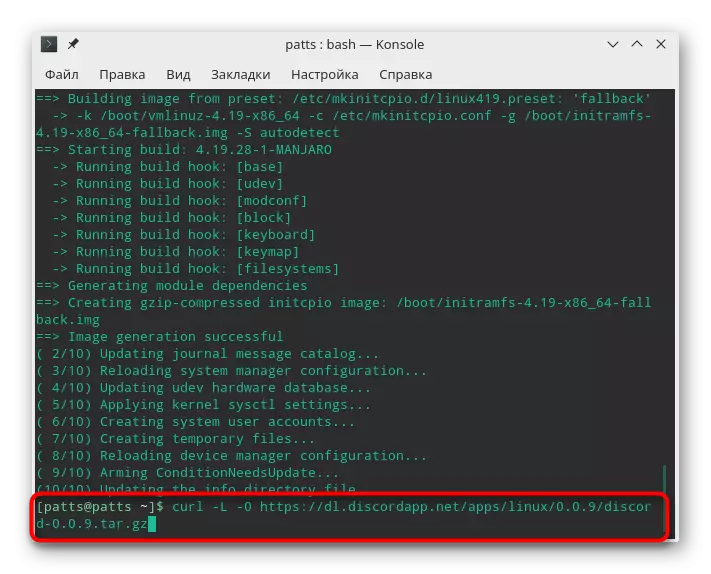
- Priority download the package found in the home directory through the curl -L -O https://dl.discordapp.net/apps/linux/0.0.9/discord-0.0.9.tar.gz. Link to download the archive TAR.GZ always indicated on the program page when viewing AUR site.
- Unpack the downloaded file into the same folder using TAR -XVF Discord-0.0.9.tar.gz, where Discord-0.0.9.tar.gz is the name of the required directory.
- Use the MAKEPKG -SRI utility to collect and immediately install the program. Upon completion of this procedure, you can go to work with software.

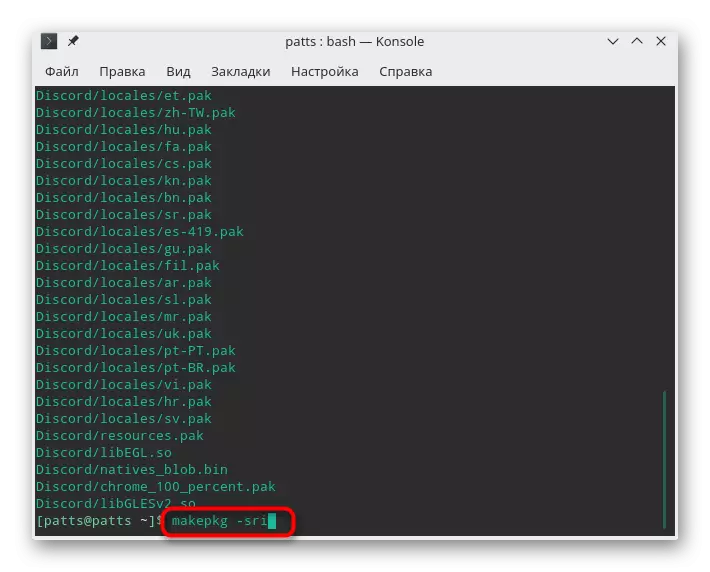
Method 3: Installing Deb Packages
The DEB file format is used to distribute software and is a standard type of data from Debian operating systems. In such distributions, the defaults are installed tools for installing the software of this format both through the graphic shell and through the "Terminal". Maximum details of all methods for adding Deb packets are painted in another our article, which you can find from the following link. As for other types of platforms, where there is no built-in utilities of installing DEB files, the installation procedure is slightly complicated.
Read more: Installing Deb Packages in Debian / Ubuntu / Mint
Redhat, Centos and Fedora
As you know, a batch manager works with RPM format based on REDHAT. Other formats are not installed using standard tools. This problems are corrected by simply conversion using an additional console application. The entire operation will take literally a couple of minutes.
- Install the utility to convert via Yum Install Alien.
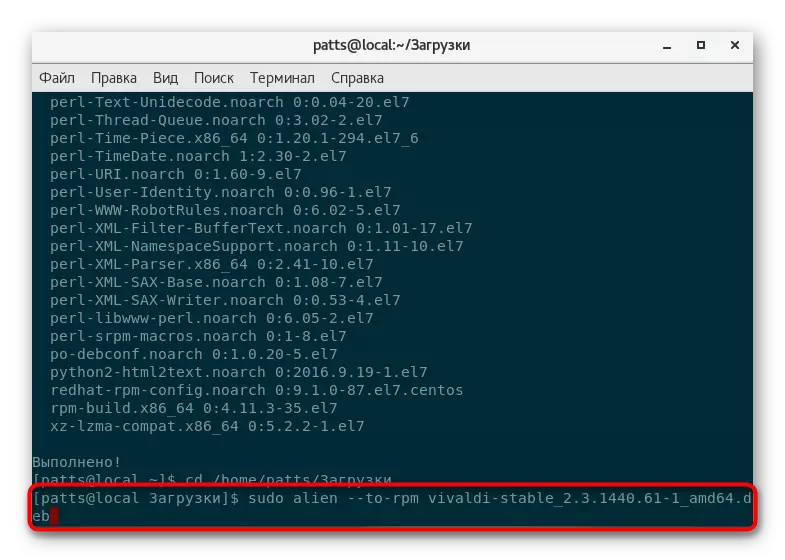
- Run the conversion process by entering Sudo Alien --to-RPM package.deb, where package.deb is the name of the required package.
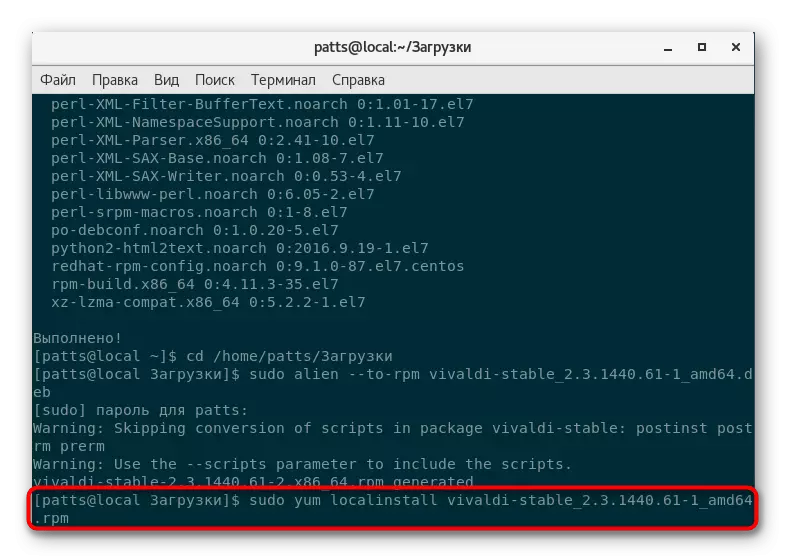
- Upon completion of the conversion, the new package will be saved to the same folder and it will only be left to unpack via sudo yum localinstall package.rpm, where package.rpm is the name of the same file, but only now the RPM format.

Arch Linux, Chakra, Manjaro
In the Arch Lixux distributions, the standard PACMAN manager is used, which was originally written to install applications with TAR.GZ extension. Therefore, to manage Deb packages, you will need to download an additional tool and add files and directories directly through it.
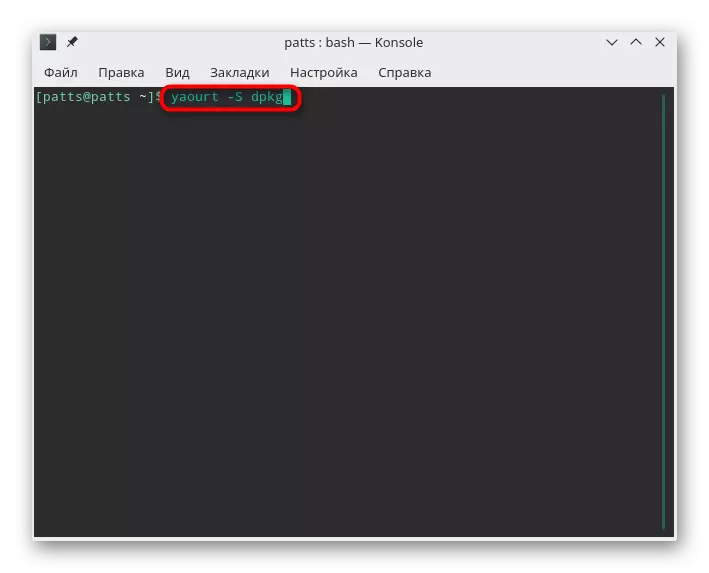
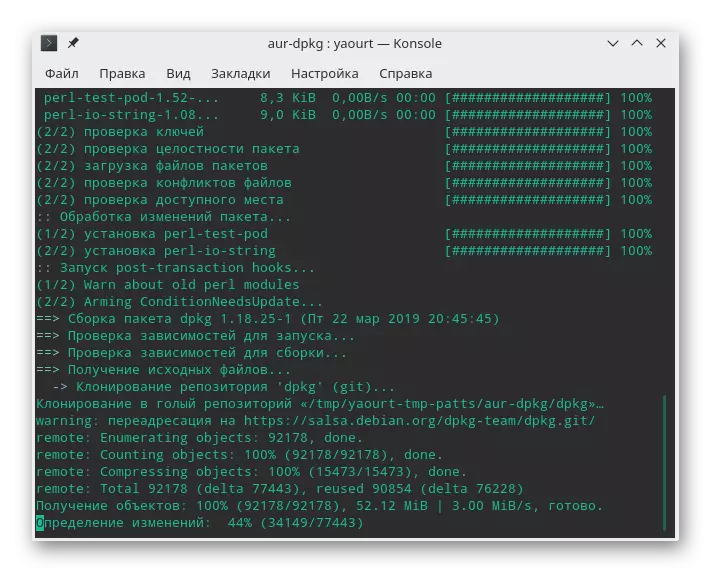
- Use Yaourt -S DPKG to download and install the utility.
- During the addition, you will need to confirm the addition of new objects several times and enter the superuser password.
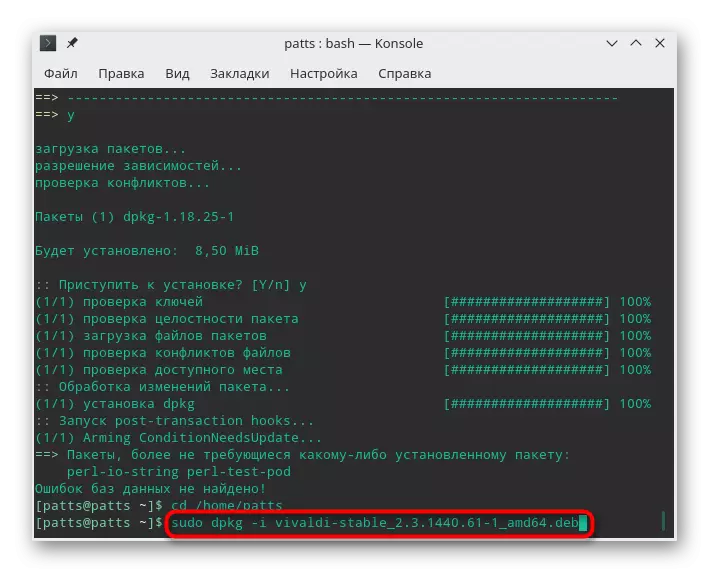
- It remains only to specify the sudo dpkg -i name_package.deb and wait for the end of the unpacking. During installation, a warning may appear on the screen on the lack of some dependencies, but it does not prevent the program to work correctly.
Method 4: Install RPM Packages
From the descriptions above, you already know that RPM packets are used by default in RedHat, CentOS and other similar distributions. As for their unpacking, the launch is available directly from the file manager. It is enough just to open the program's storage folder and run it double-clicking the left mouse button. The installation will start, and upon completion of it, you can find the application through the menu or open it through the entry of the appropriate command in the console. In addition, to search for software, the same standard software "Installing applications" is perfect.
To unpack the RPM packets in Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint distributions are commonly used additional tools, but only in cases where it is not possible to find a similar DEB package on the network. Deployed Instructions on this topic can be found in the article Next.
Read more: Installing RPM packets in Ubuntu / Debian / Mint
In Arch Linux, Chakra, Manjaro, there is no normal utility, which would have converted RPM packets to a supported TAR.GZ format. Therefore, we can only advise you to search for the same program in supported expansion. It is best to do this at the official source of AUR.Archlinux.org, where there are links to download most popular applications from the developers or mirrors with the TAR.GZ archive.
Method 5: Installing programs in the archives TAR.GZ
According to the standard, let's start with distributions on Debian. In this case, TAR.GZ is set by compiling the contents of the archive to the new DEB package. The whole procedure is divided into four simple steps, and you can familiarize yourself with them in separate our material on the following link.
Read more: Installing TAR.GZ format files in Ubuntu / Debian / Mint
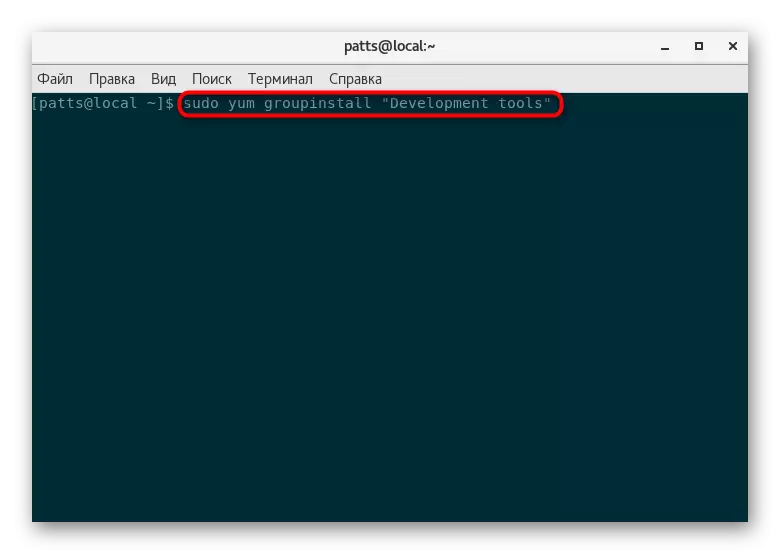
In RedHat, adding through the compilation of the configuration file looks a bit differently:
- First, add to the system of development to the system: sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools".
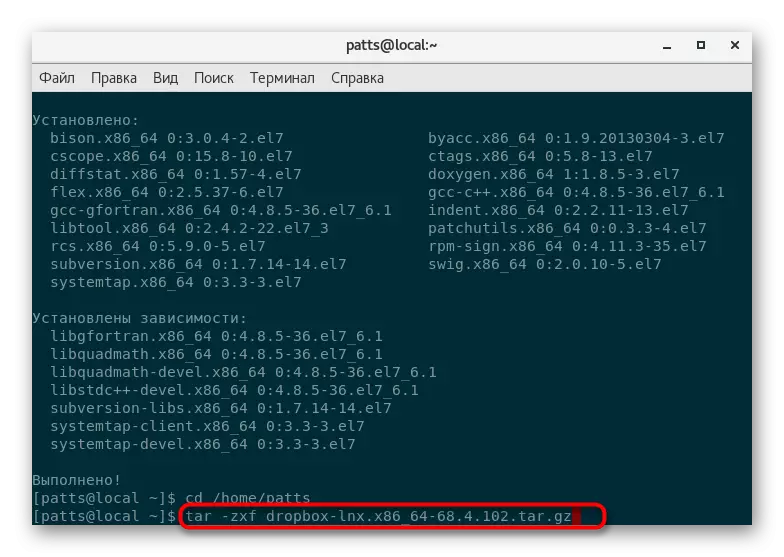
- Then unpack the available archive via TAR -ZXF Archive_name.tar.gz.
- Upon completion of the unzipping, move to the finished folder via CD Archive_Name and follow these commands alternately:
./configure.
Make
Sudo Make Install.
After that, you can run the application and interact with it.
As far as you know, the packet manager PACMAN is default normally with the archives of the TAR.GZ format, so when using Arch, Chakra or Manjaro, you should perform the appropriate instructions from the method 2.
Today you have been acquainted with five different methods of installing software in operating systems based on Linux kernel. As you can see, for each distribution you need to use the appropriate method. We also recommend paying time to find the search required for the format, so that the installation operation is as quickly and simple.
