
Sometimes the user has a need to track the list of running processes in the Linux operating system and find out the most detailed information about each of them or some specifically. There are built-in tools in the OS, allowing to carry out the task without any effort. Each such tool is focused under its user and opens various opportunities for him. Within the framework of this article, we will touch on two options that will be useful in certain situations, and you will only have to choose the most suitable.
We view the list of processes in Linux
Practically in all popular Linux-based distributions, the processes list opens and viewed using the same commands, tools. Therefore, we will not focus on individual assemblies, and take for example the latest version of Ubuntu. You will also have only to fulfill the instructions provided that the entire procedure has passed successfully and without difficulties.Method 1: Terminal
Undoubtedly, the classical operating system console on Linux plays a crucial role when interacting with programs, files and other objects. All major manipulations of the user produces through this application. Because from the very beginning I would like to tell about the output of information through the Terminal. We will pay attention only to one team, however, consider the most popular and useful arguments.
- To start, start the console by clicking on the corresponding icon in the menu or using the Ctrl + Alt + T keys combination.
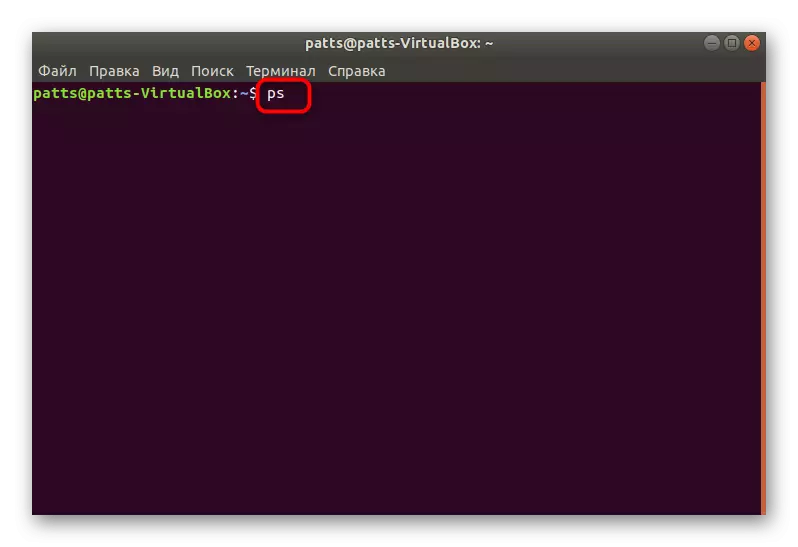
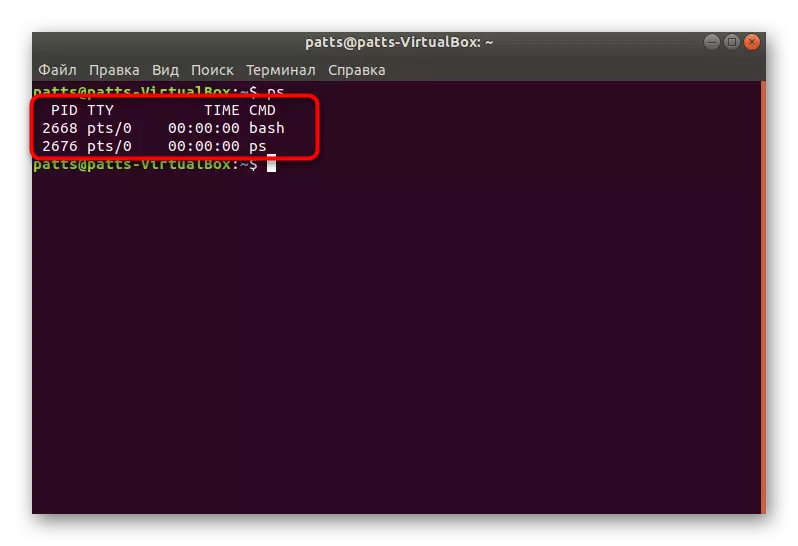
- Sunday the PS team to simply make sure of it and familiarize yourself with the type of data shown without the use of arguments.
- As you can see, the list of processes turned out to be small enough, it is usually no more than three results, so it is worth paying the time already mentioned arguments.
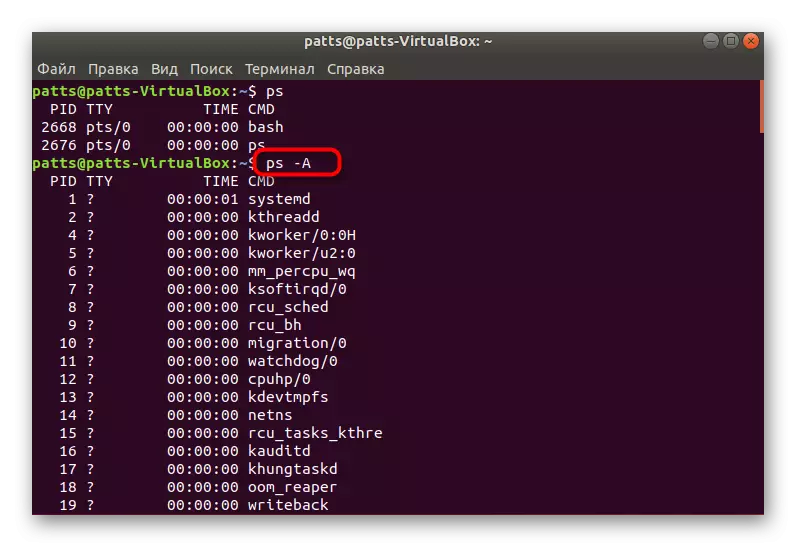
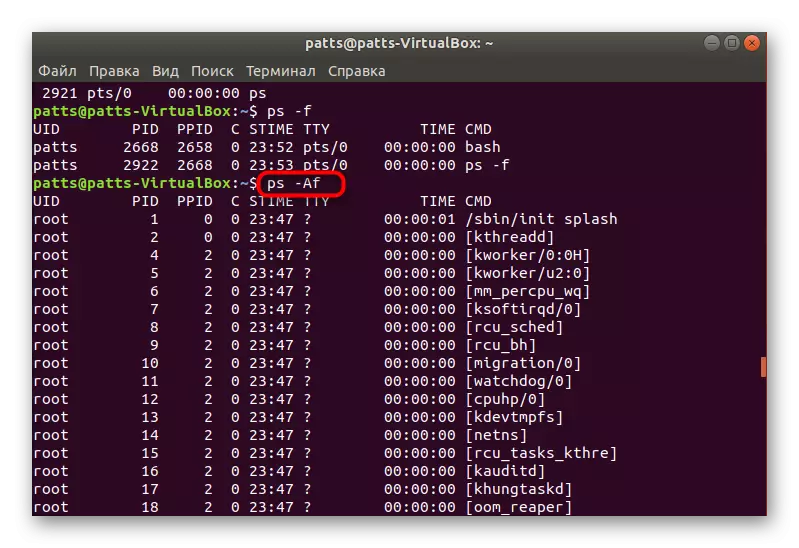
- To display all the processes at once, it is worth adding. In this case, the command looks like PS -A (a must be in the upper case). After pressing the Enter key, you will immediately see the lines.
- The previous team does not displays the group leader (the main process from the bundle). If you are interested in this data, here you should register PS -D.
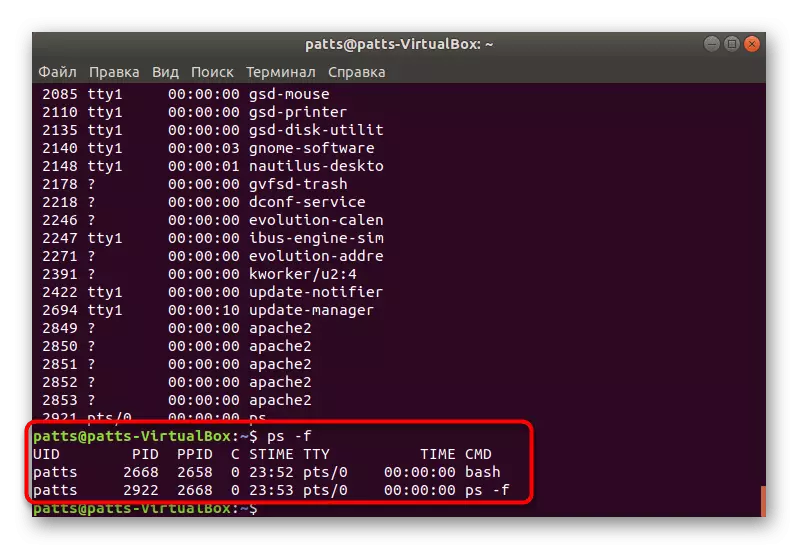
- You can get more useful information by simply adding -f.
- Then the full list of extended information processes will be called through PS -AF. In the table you will see the UID - the name of the user running the process, the PID is a unique number, PPID - the parent process number, C - the amount of load time on the CPU in percent, when the process is active, Stime is the activation time, TTY - the console number from where it was perfect Running, Time - Opening hours, CMD is a command that runs the process.
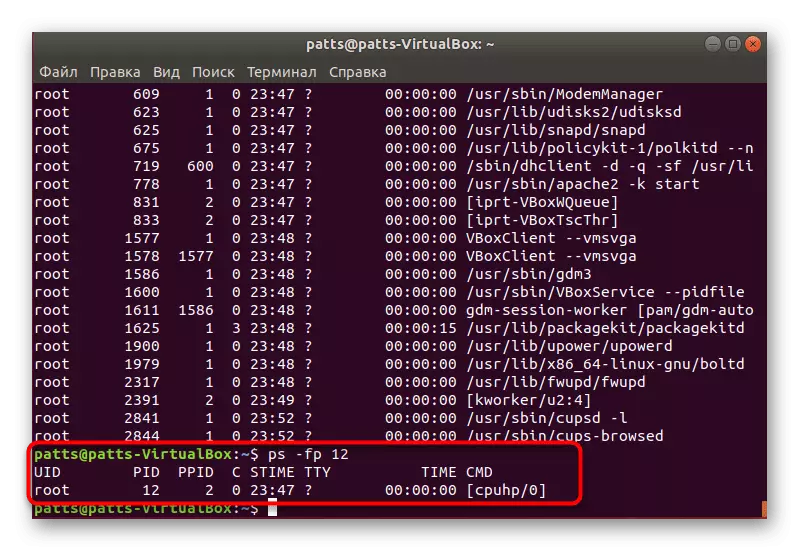
- Each process has its PID (Proccess Identificator). If you want to see a summary of a specific object, suck the PS -FP PID, where the PID is the process number.
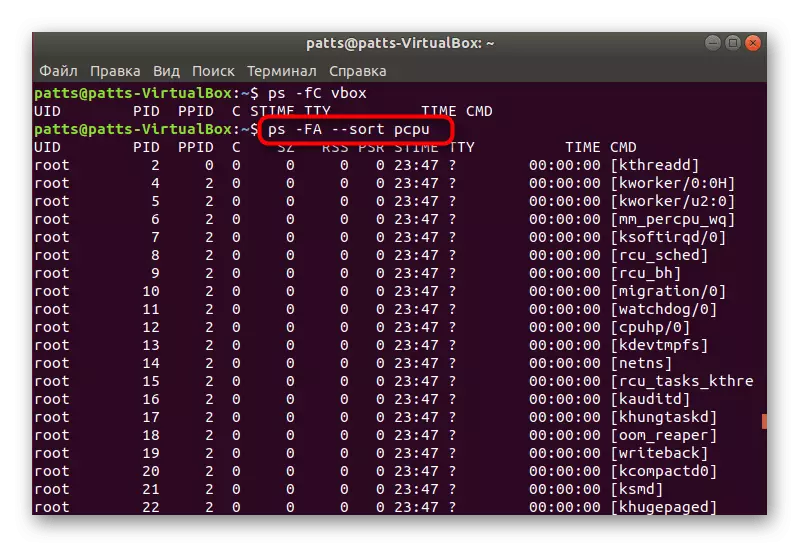
- Separately, I would like to affect and sort. For example, the PS -FA -Sort PCPU command allows you to put all the lines in the CPU load order, and the PS -FE --SORT RSS software is based on the volume of RAM.

We talked about the main arguments of the PS command, however, there are also other parameters, for example:
- -H - mapping tree of processes;
- -V - output versions of objects;
- -N - sample of all processes other than those specified;
- -We - display only by the command name.
To view the method of viewing processes through the built-in console, we chose the PS command, and not TOP, since the second is limited to the size of the window and the not fitting data is simply ignored, while remaining unfinished.
Method 2: System Monitor
Of course, the method of viewing the desired information through the console is complex for some users, but it allows you to get acquainted with all the important parameters and apply the necessary filters. If you want to simply view a list of running utilities, applications, as well as make a number of interactions with them, you will fit the built-in graphical solution "System Monitor".
You can find out this application in another article by clicking on the following link, and we go to the fulfillment of the task.
Read more: Methods for launching a system monitor in Linux
- Run the "System Monitor" by any convenient method, for example, through the menu.
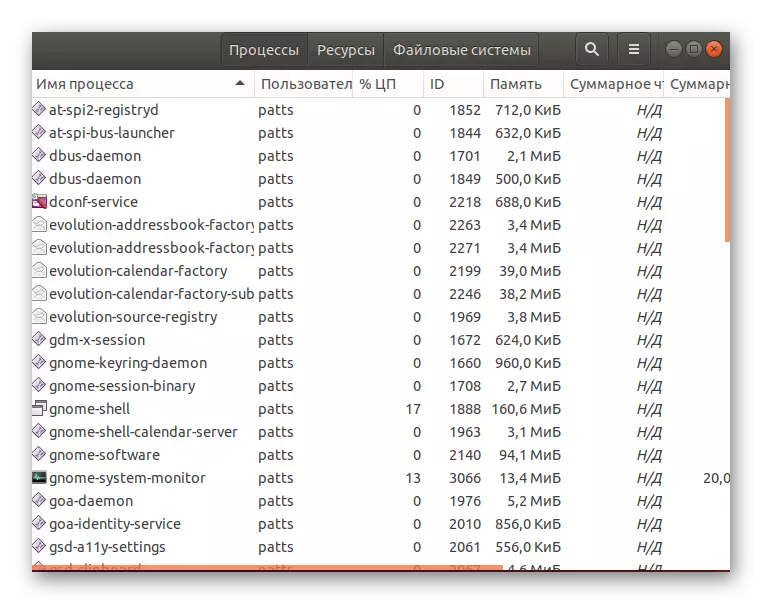
- Immediately the list of processes will immediately appear. You will learn how much they consume memory and resources of the CPU, you will see a user who has running execution of the program, as well as be familiar with other information.
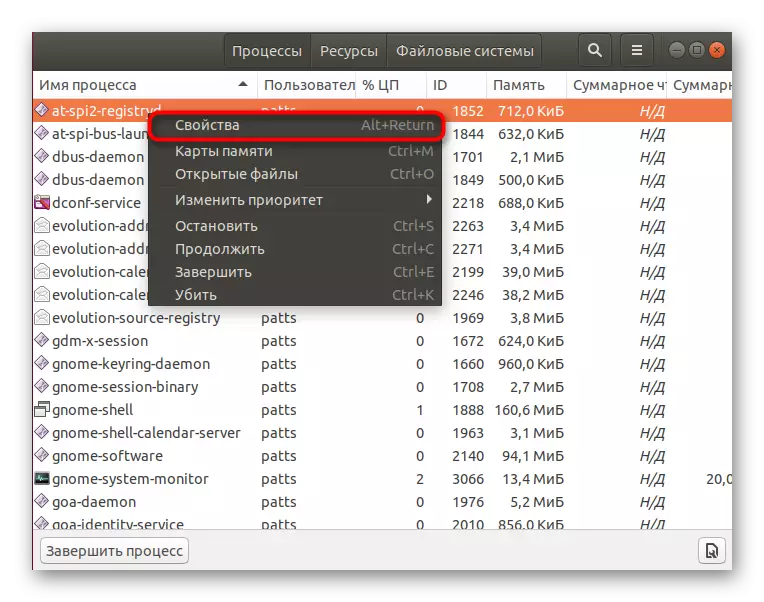
- Right-click on the line of interest to go to its properties.
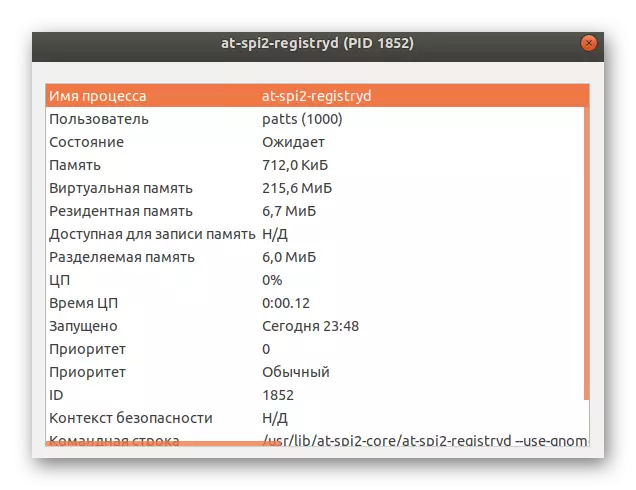
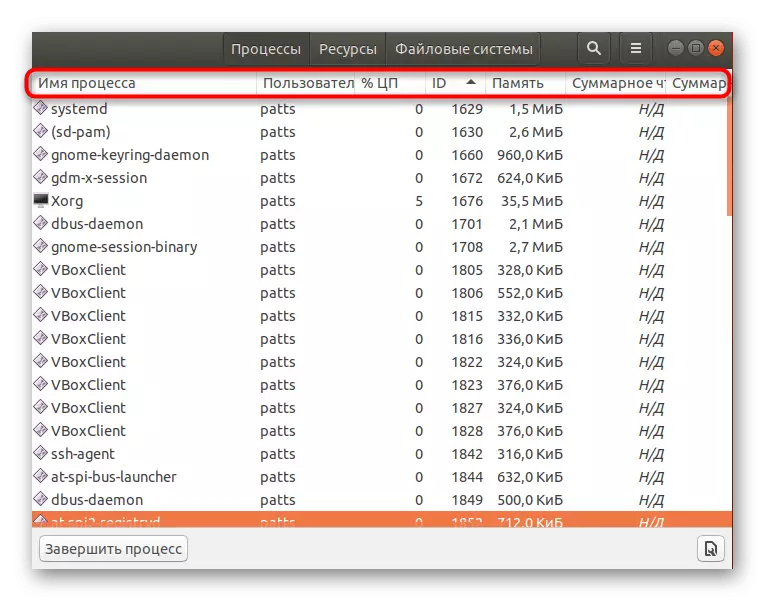
- Almost all the same data are displayed here that are available to obtaining through the "Terminal".
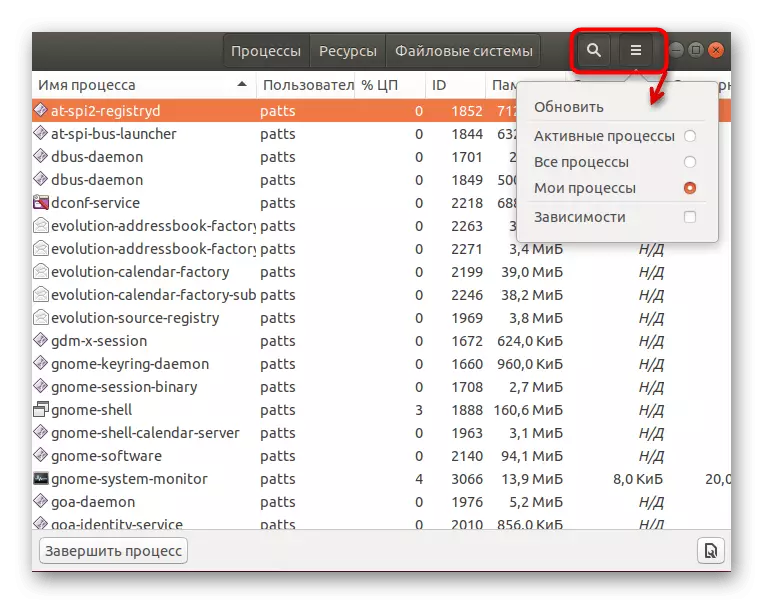
- Use the search or sort function to find the desired process.
- Pay attention to the top panel - it allows you to sort the table on the necessary values.
Completion, stop or deleting processes also occurs through this graphic application by pressing the appropriate buttons. For novice users, such a solution will seem more convenient than working in the Terminal, but the development of the console will allow to receive the desired information not only faster, but also with a large number of parts.
