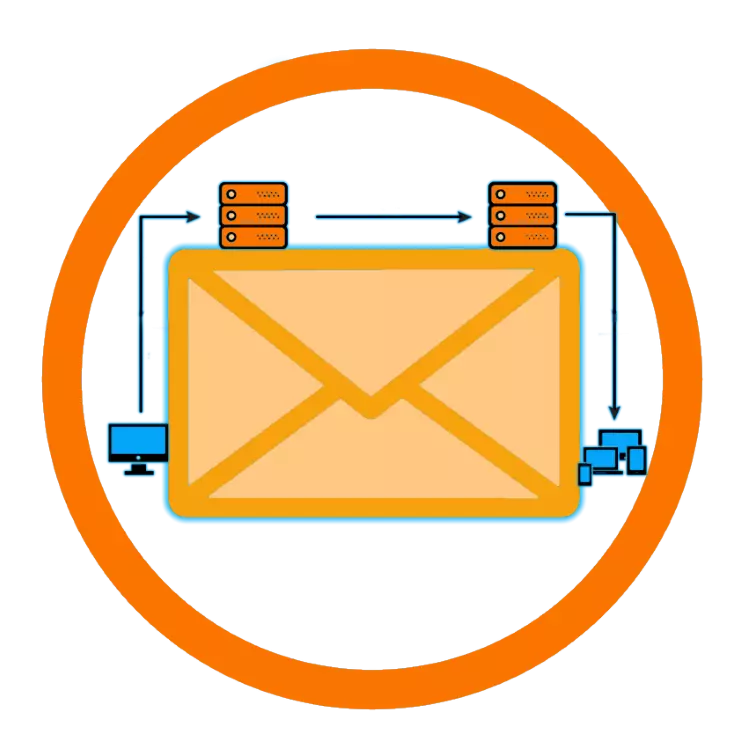
Many users, facing the need to configure this or that mail client, are asked: "What is the email protocol". Indeed, to "force" such a program to function normally, and then it is comfortable to use it, it is important to understand which of the available options should be chosen, and what is the difference from the rest. It is about postal protocols, the principle of their work and the scope of application, as well as some other nuances will be told in this article.
Email Protocols
In total, there are three generally accepted standards used to exchange emails (sending and receiving them) - this is IMAP, POP3 and SMTP. There is still an HTTP, which is often called Web-mail, but it does not have a direct relationship to our today's topic. Below will consider in more detail each of the protocols, determining their characteristic features and possible differences, but before we give the definition of the term itself.
The email protocol, if you say the most simple and understandable language - this is exactly how the exchange of electronic correspondence is made, that is, what path and with what "stops" is a letter from the sender to the recipient.
SMTP (Simple Mail TRANSFER PROTOCOL)
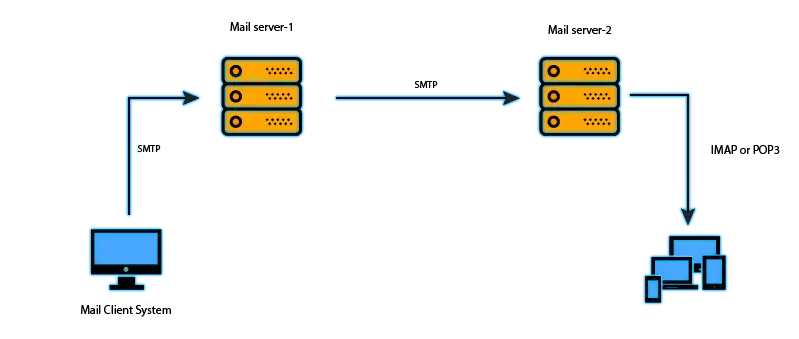
Simple mail transfer protocol - this is how the full name SMTP is translated and decrypted. This standard is widely used to transmit e-mail in TCP / IP networks (specifically to transfer outgoing mail TCP 25). There is also its more "new" variety - the ESMTP extension (Extended SMTP) adopted in 2008, although it is not separated from Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
The SMTP protocol is used by mail servers and agents for sending and receiving letters, but applications-customers-oriented applications use it only in one direction - sending emails to the server for their subsequent relay.
Most postal applications, which include well-known Mozilla Thunderbird, The Bat!, Microsoft Outlook, use either POP, or IMAP, which will be discussed later. In this case, a proprietary protocol can use the proprietary protocol to access the user account on its own server to gain access to the user account on its own server, but this is already out of the scope of our topic.
See also: Troubleshooting letters by email
POP3 (Post Office Protocol Version 3)
The post office protocol of the third version (translated from English) is an application-level standard that is used by customer specialized program programs to obtain e-mail from a remote server by means of the same type of connection as in the case of SMTP - TCP / IP. Directly in its work POP3 uses the port at number 110, however, 995 is used with SSL / TLS connections.
As mentioned above, it is this email protocol (as well as the next representative of our list) is most commonly used to directly retrieve mail. Not least, this is justified by the fact that POP3, along with IMAP, not only supported by most of the specialized postal programs, but also is used by the leading providers of the relevant services - Gmail, Yahoo!, Hotmail, etc.
Note: The standard in the field is the third version of this protocol. The first and second one to it (POP, POP2, respectively), are considered morally outdated.
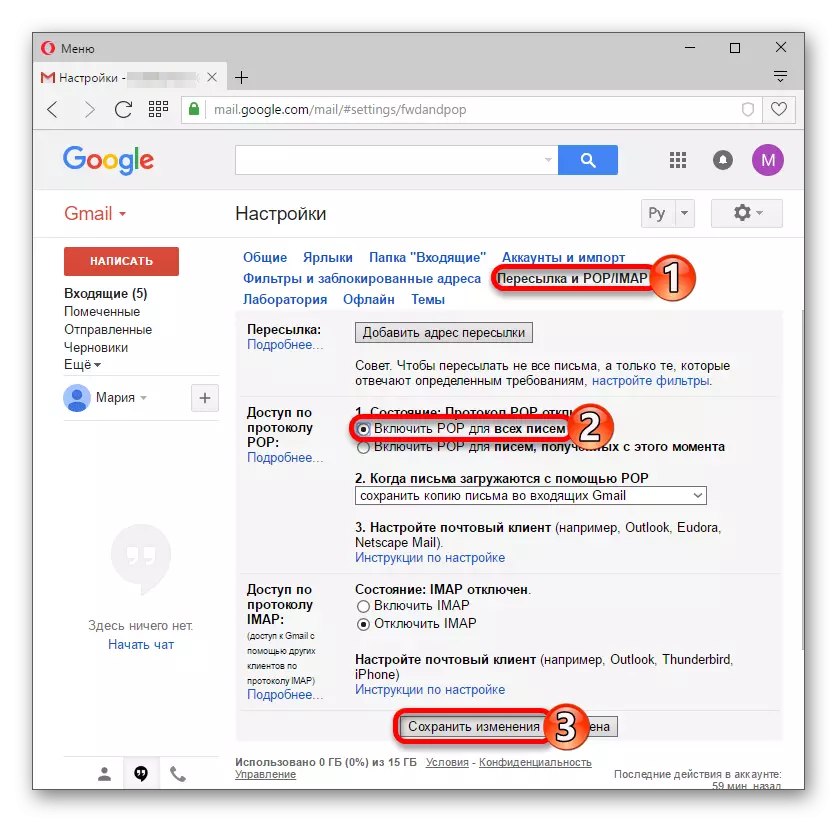
READ ALSO: Gmail Mail Setup in the Post Client
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
This is an application-level protocol used to access electronic correspondence. As the standards considered by us above, the IMAP is based on the TCP transport protocol, and to perform the tasks assigned to it, port 143 (or 993 for SSL / TLS connections) is used).
Actually, it is the Internet Message Access Protocol that provides the widest opportunities for working with letters and directly by postal boxes placed on the central server. A client application that uses this protocol for its work has full access to electronic correspondence as if it is stored not on the server, but on the user's computer.
IMAP allows you to perform all the necessary actions with letters and drawers (drawers) directly to the PC without the need to constantly send to the server attached files and text content and back to them. The POP3 considered above, as we already designated, it works somewhat differently, "tightening" the necessary data when connected.
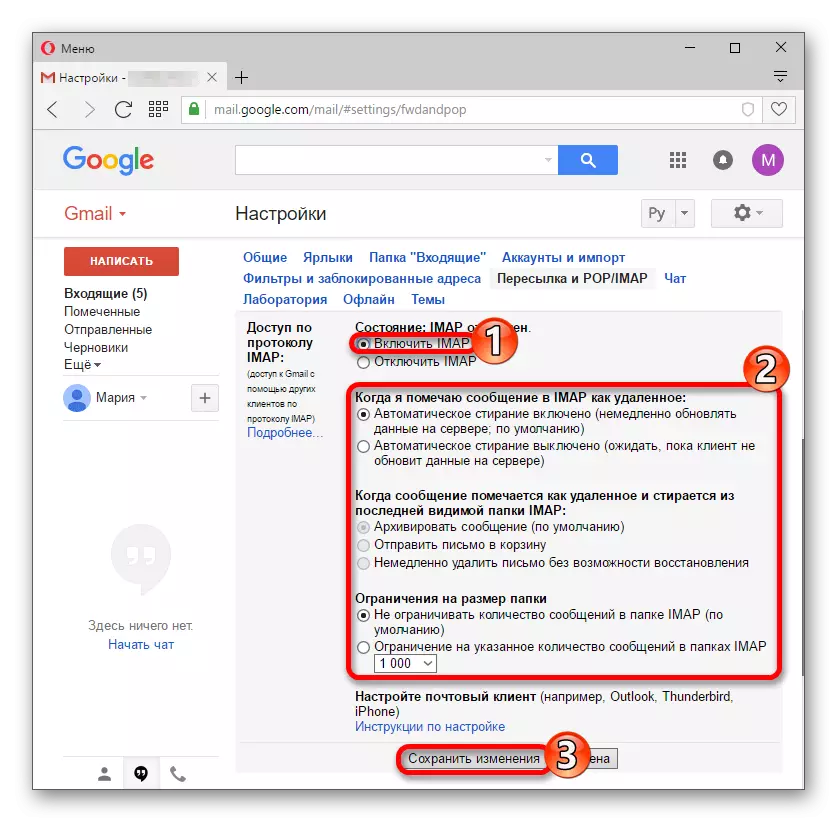
See also: Solving problems with sending emails
Http.
As mentioned at the very beginning of the article, HTTP is a protocol that is not intended to communicate by email. At the same time, it can be used to access the mailbox, drawing up (but not sending) and receiving electronic letters. That is, it performs only part of the functions characteristic of the postal standards discussed above. And yet, even at the same time, it is often called webmail. Perhaps a certain role in this was played by the once popular service hotmail, which uses HTTP.Select email protocol
So, having familiarized yourself with what is each of the existing postal protocols, we can safely switch to the immediate choice of the most appropriate. HTTP, due to the reasons designated above, does not represent interest in this context, and SMTP is focused on solving tasks other than those who push the ordinary user. Therefore, when it comes to setting up and ensuring the correct work of the mail client, you should choose between POP3 and IMAP.
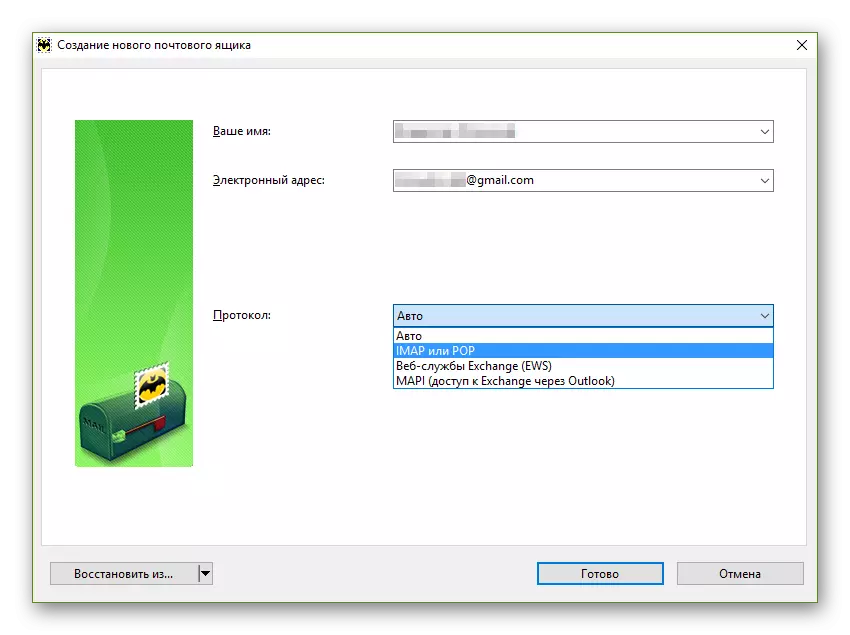
Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
In the event that you wish to have operational access to all, not even the most relevant e-mail, we strongly recommend to stop your choice on IMAP. To the advantages of this protocol, you can classify the established synchronization, allowing you to work with mail on different devices - both at the same time, and in the order of the queue, thanks to which the necessary letters will always be at hand. The main disadvantage of Internet Message Access Protocol follows from the features of its operation and is a relatively rapid filling of disk space.
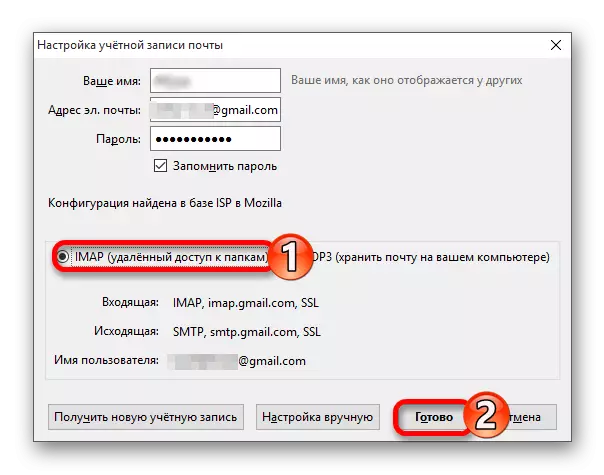
IMAP and other, no less important advantages - it allows you to organize letters in the postage program in a hierarchical order, create separate directory and put messages there, that is, to perform their sorting. Due to this, it is possible to quite easily organize efficient and comfortable work with electronic correspondence. However, one more disadvantage follows from such a useful function - along with the consumption of free space on the disk, there is an increased load on the processor and the RAM. Fortunately, this is noticeable only in the synchronization process, and exclusively on low-power devices.
POST OFFICE PROTOCOL 3 (POP3)
POP3 is suitable for setting up the mail client if the presence of a free space on the server (drive) and high speed of work plays a paramount role. It is important to understand the following: stopping your choice on this protocol, you refuse to synchronize between devices. That is, if you received, for example, three letters on the device number 1 and noted them as read, on the device number 2, also working on Post Office Protocol 3, they will not be marked as such.
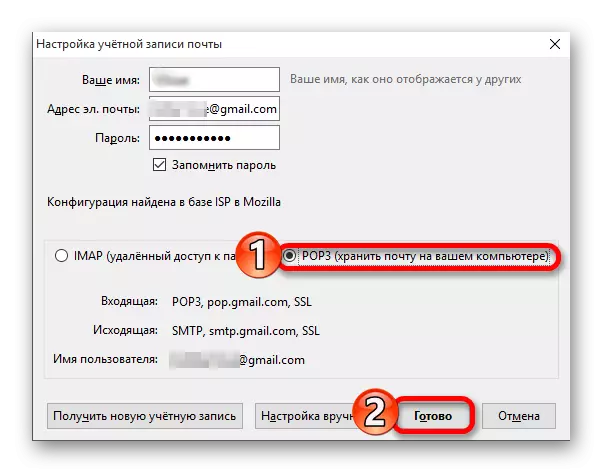
The advantages of POP3 consist not only in saving disk space, but also in the absence of at least a few noticeable load on the CPU and RAM. This protocol, regardless of the quality of the Internet connection, allows you to upload electronic letters entirely, that is, with all textual contents and investments. Yes, this happens only when connected, but here is a more functional IMAP, subject to limited traffic or low speed, the messages will only be partially, and only their headers will show at all, and most of the content will leave on the server "up to better times".
Conclusion
In this article we tried to give the most detailed and understandable answer to the question, what is the email protocol. Despite the fact that all of them there are four, only two - IMAP and POP3 are of interest for an ordinary user. The first will interest those who are used to using mail from different devices, to have quick access absolutely to all (or necessary) letters, organize them and organize them. The second is more narrow-controlled - much faster in work, but not allowing to organize it at once on several devices.
