
All utilities, programs and other libraries in Linux operating systems are stored in packages. You download such a directory from the Internet in one of the available formats, then add to the local storage. Sometimes it may be necessary to view a list of all present programs and components. The task is carried out by different methods, each of which will be most suitable for different users. Next, we will analyze each option by taking the Ubuntu distribution for the example.
We view the list of installed packages in Ubuntu
The Ubuntu also has a graphical interface implemented by default on the GNOME shell, as well as the usual "terminal" through which the entire system is managed. Through these two components, view the list of added components is available. The choice of the optimal method depends only on the user itself.Method 1: Terminal
First of all, I would like to pay attention to the console, since the standard utilities present in it allow you to use all the functionality at the maximum. As for the display of the list of all objects, it is done quite easily:
- Open the menu and run the "Terminal". It is also done by the clap of the hot key Ctrl + Alt + T.
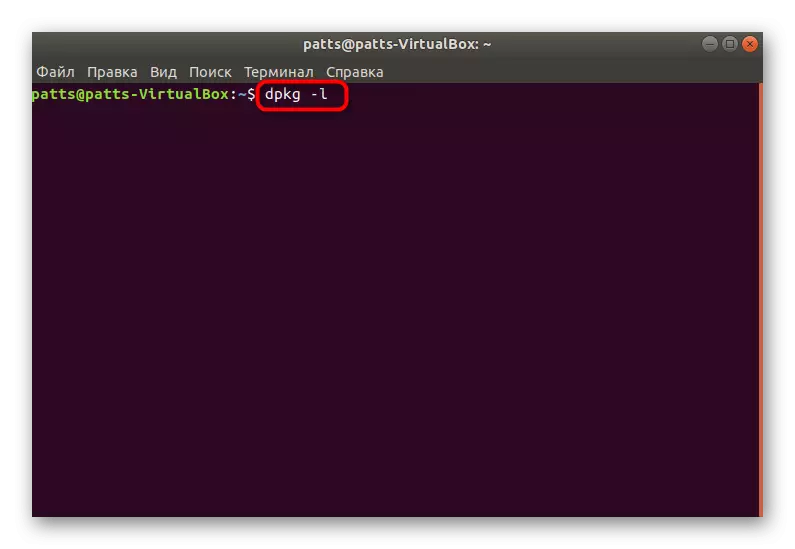
- Use the standard DPKG command with the -L argument to display all packets.
- Using the mouse wheel, move the list by viewing all the files found and libraries.
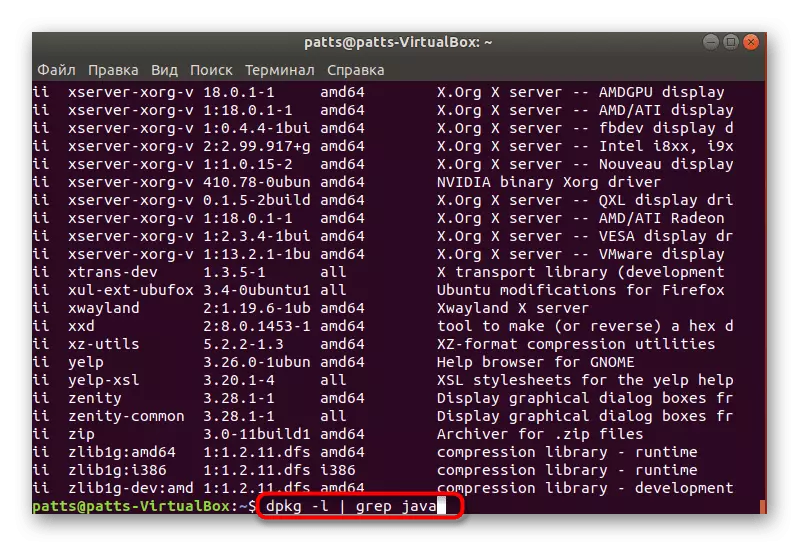
- Add another command to DPKG -L to search for a specific value on the table. Looks like a line like this: dpkg -l | Grep Java, where Java is the name of the required package.
- Found suitable results will be highlighted in red.
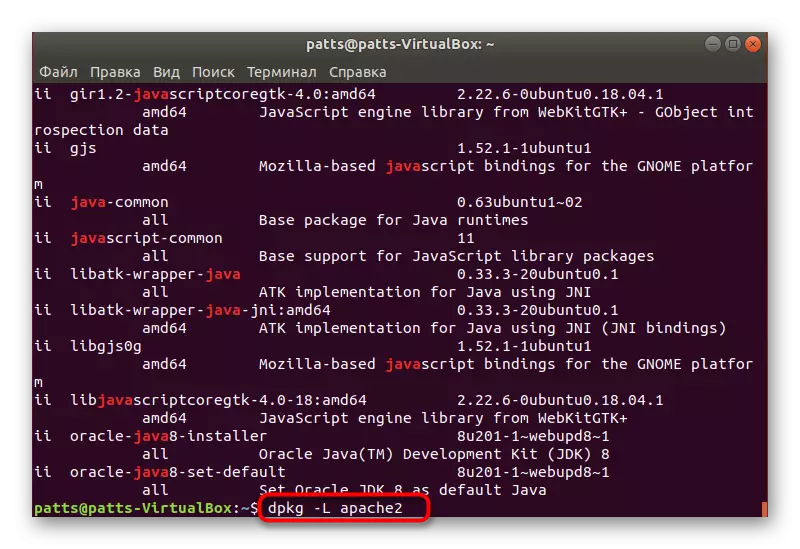
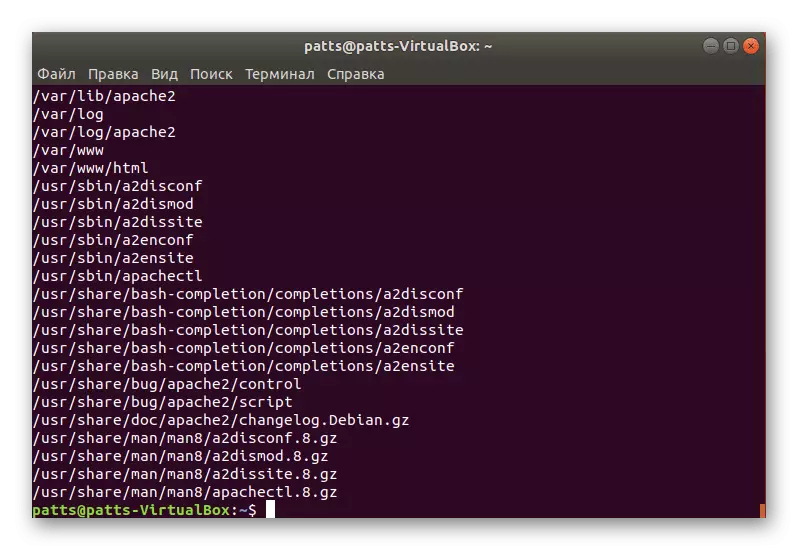
- Use DPKG -L Apache2 to get information about all files installed through this package (Apache2 - the name of the search packet).
- A list of all files with their location will appear.
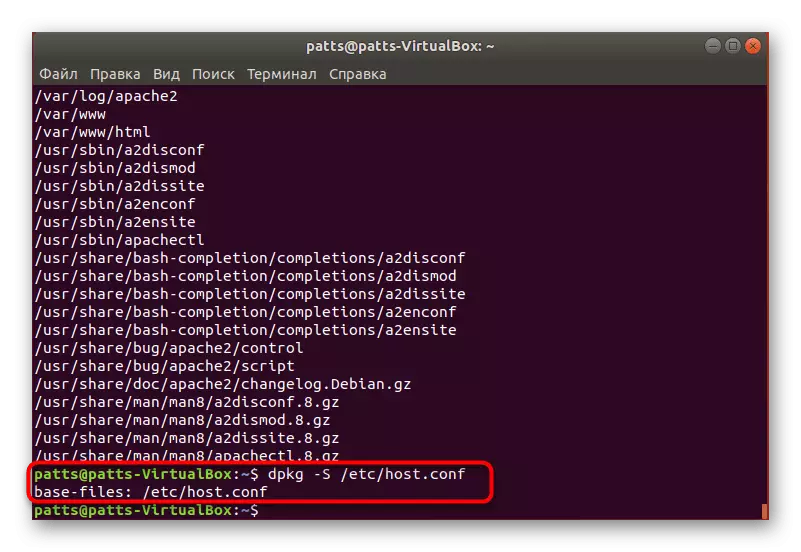
- If you want to know how a specific file was added, you should enter dpkg -S /etc/host.conf, where /etc/host.conf is the file itself.
Unfortunately, not everyone is convenient to use the console, and it is also not always required. That is why it is necessary to bring an alternative to display a list of packages present in the system.
Method 2: Graphic Interface
Of course, the graphical interface in Ubuntu does not fully implement the same operations that are available in the console, but the visualization of the buttons and utilities greatly simplifies the task execution especially for inexperienced users. First we advise contact the menu. There are several tabs, as well as sorting to show all programs or only popular. The search for the desired package can be done through the corresponding string.
Application Manager
"Application Manager" will allow you to study the question in more detail. In addition, this tool is set by default and provides quite wide functionality. If for any reason "Application Manager" is missing in your version of Ubuntu, check out the other article by clicking on the following link, and we go to the search for packages.
Read more: Installing Application Manager in Ubuntu
- Open the menu and run the desired tool by clicking on its icon.
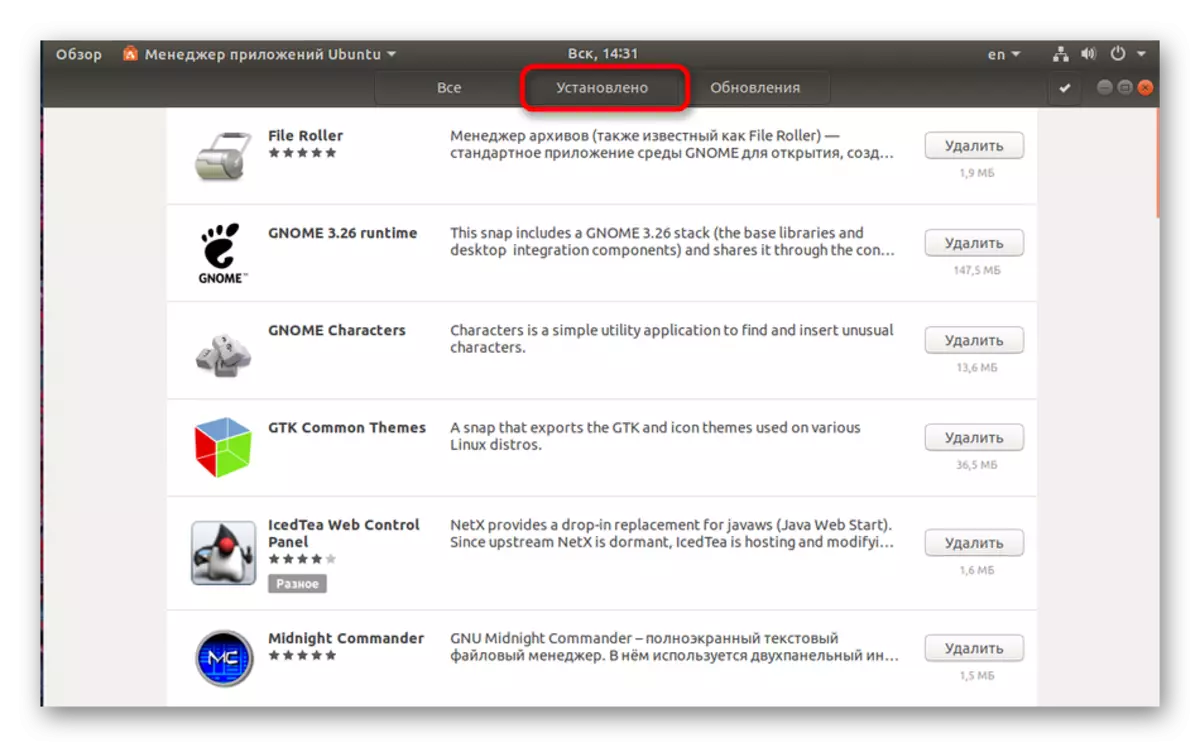
- Go to the "Installed" tab to cut off that software that is not yet available on the computer.
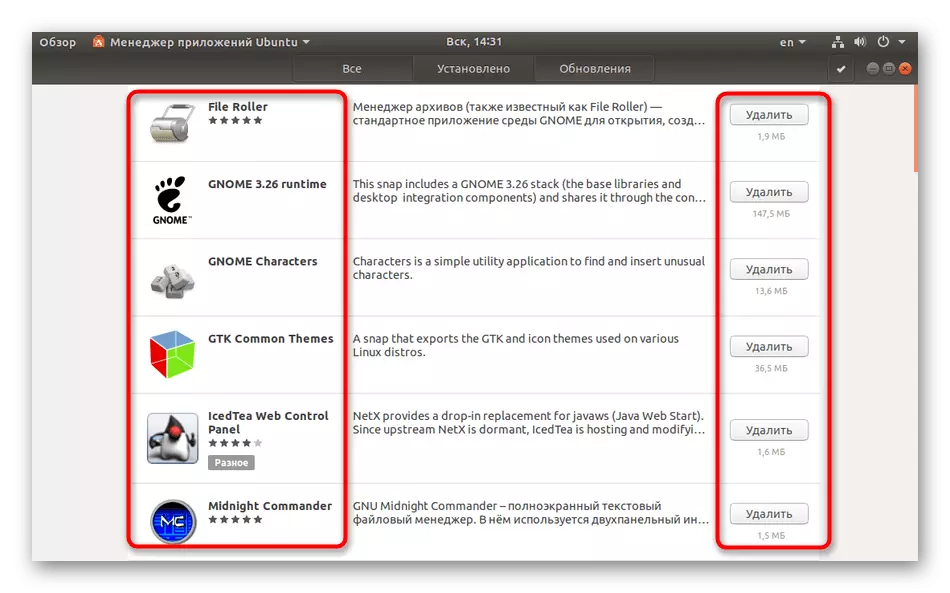
- Here you see the name of software, a short description, size and button that allows you to quickly delete.
- Click on the program name to go to its page in the manager. It is familiar with the possibilities of software, its launch and uninstalling.
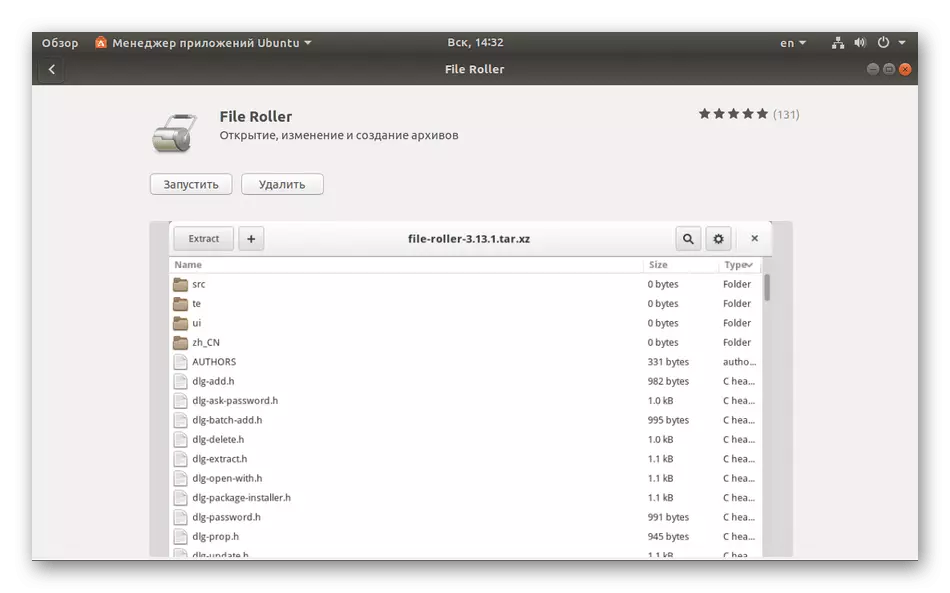
As you can see, work in the "Application Manager" is quite simple, but the functionality of this tool is still limited, so a more advanced option will come to the rescue.
Synaptic package manager
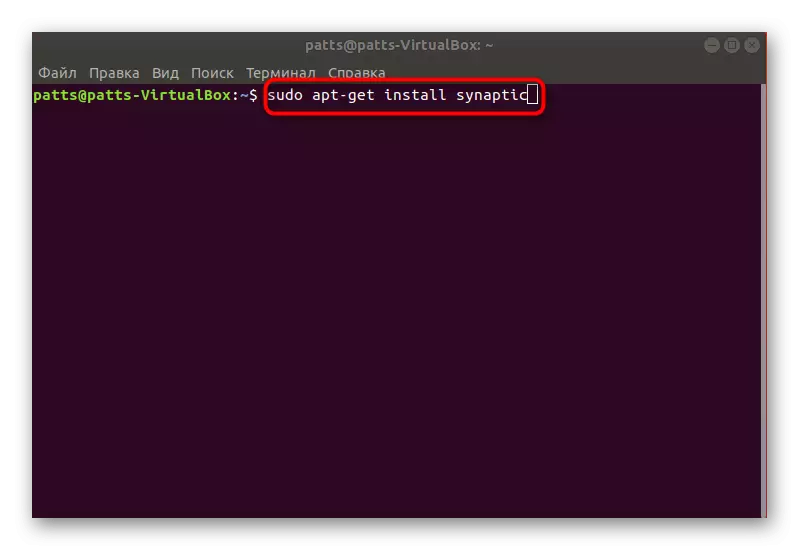
Installing an additional SYNAPTIC package manager will allow you to receive the detailed information about all added programs and components. To begin with, it will still have to use the console:
- Run the Terminal and enter the Sudo APT-Get Synaptic command to install Synaptic from the official repository.
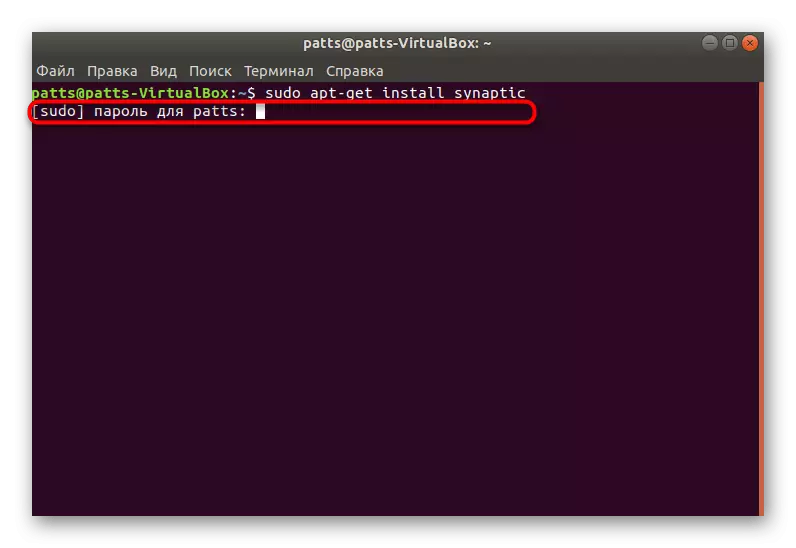
- Specify your password for root access.
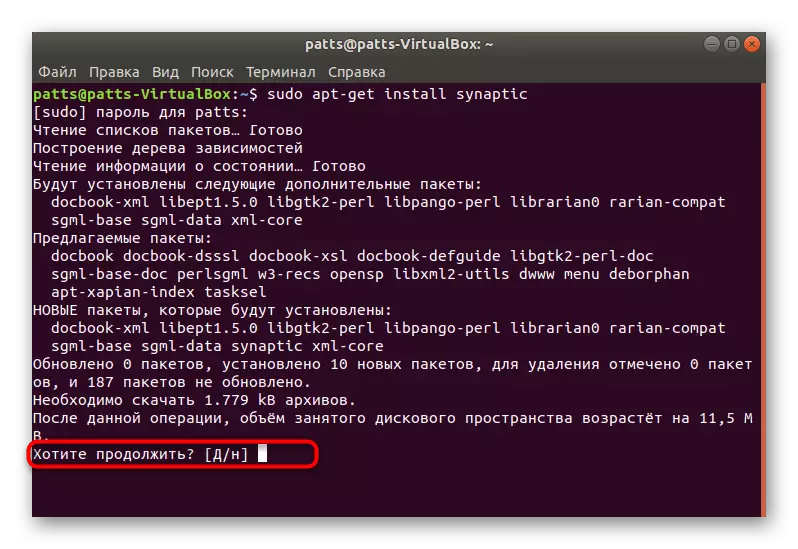
- Confirm Adding new files.
- Upon completion of the installation, run the tool through the Sudo Synaptic command.
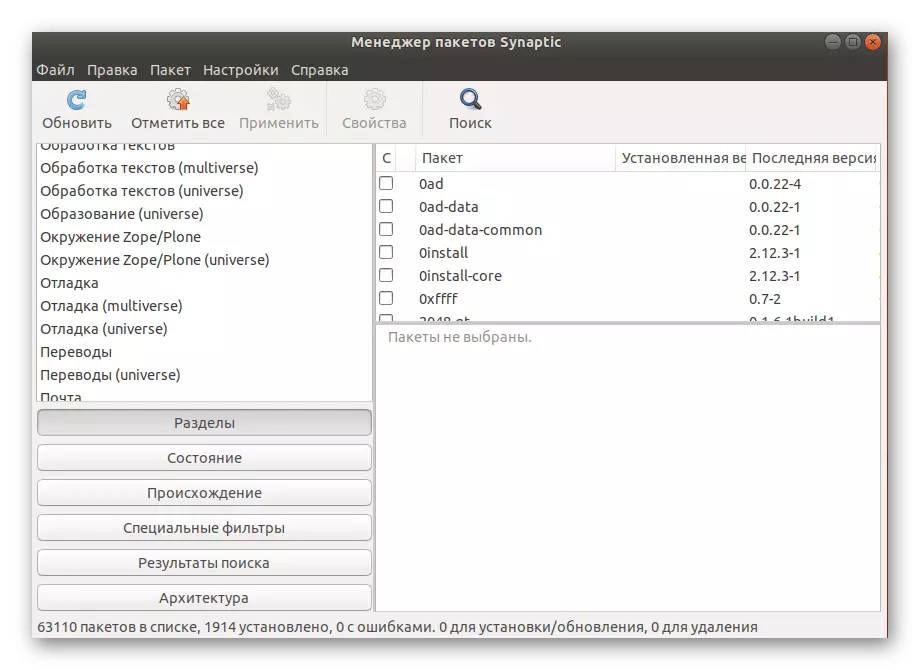
- The interface is divided into several panels with various sections and filters. Select the appropriate category on the left, and see all the installed packages and detailed information about each of them on the right in the table.
- There is also a search function that allows you to immediately find the required data.
None of the above methods will be able to find a package, during the installation of which certain errors have occurred, so closely follow the emerging notifications and pop-up windows during unpacking. If all attempts ended with failure, then there is no desired package in the system or has another name. Check the name with what is indicated on the official website, and try reinstalling the program.
