
As you know, in Linux operating systems, there is a huge number of built-in terminal commands performing a wide variety of actions. Some of them allow you to install programs, others are designed to manage logical volumes and hard drives. There are among them and those that are created to interact with files. One of these commands is called Touch, and it is about it that we want to tell in the framework of this training material.
We use the touch command in Linux
To use the touch command in Linux, you will need to examine its syntax and understand the principles of input. There should be no problems with this, since the utility itself is quite simple, and with accessible options can be sorted out literally in a few minutes. Let's just start with this.Syntax
Pay attention to the standard view of the string when entering the Touch command. It looks like this: Touch + [options] + file. If the action must be implemented on behalf of the superuser, you will have to add sudo at the beginning of the line, and after it is activated to write a password confirming the account. As for additional options, it is worth noting the following:
- --Help and --Version are rarely used. The first option will give the opportunity to read the official documentation, and the second will display the current version of the utility.
- -a is responsible for changing the access time to the specified file.
- -m changes the modification time.
- -C determines that the object with the specified name will not be created.
- -R will allow you to use the access time and modification of the specified file.
- -t is designed to change the date and time by manually input.
- -D uses the date and time specified in the form of a string.
Now you know absolutely about all the available options in question today. Let's go to the study of the parameters to deal with all the basic actions performed using this utility.
Generation of empty files
To begin with, we'll figure it out with the action of the touch command without using any arguments - so it creates an empty file size 0 bytes with the specified name.
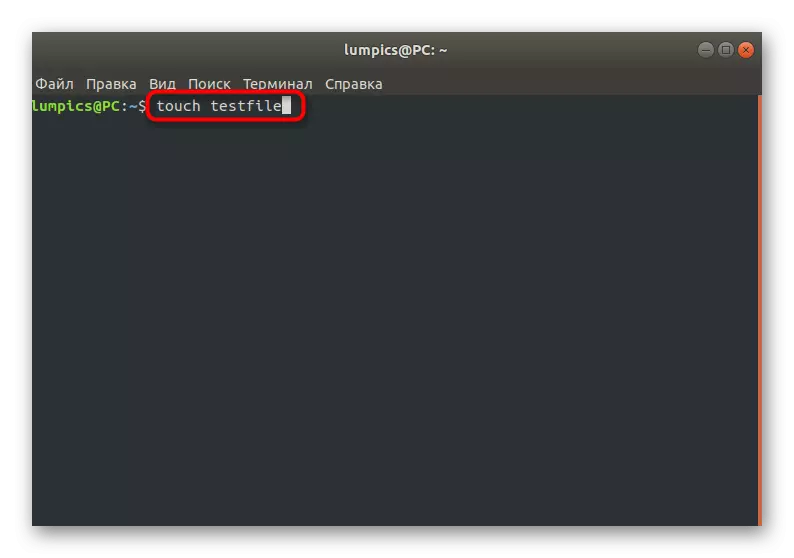
- Open the "Terminal" convenient for you, for example, through the icon in the application menu or the Ctrl + Alt + T. key combination.
- Here enter Tuesch Testfile, where TestFile replace the necessary name.
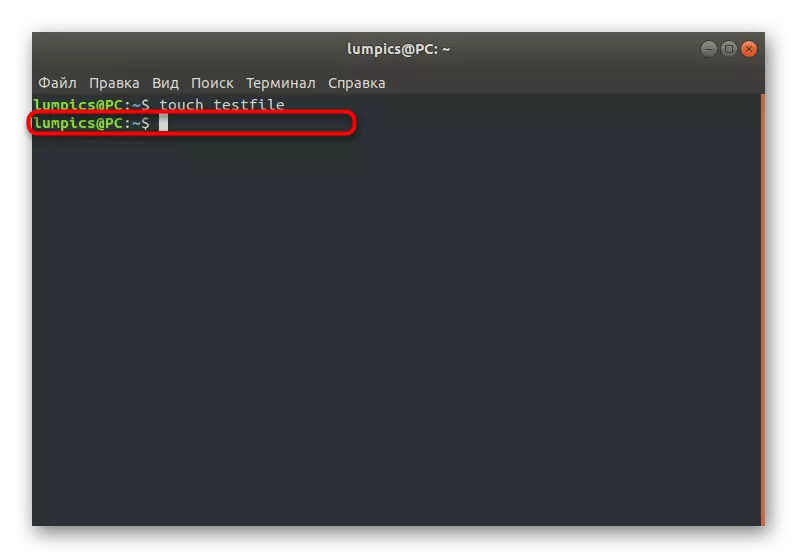
- After activating this command, if it passed without any errors, a new line will appear for input, and in the current location the corresponding object will be created.
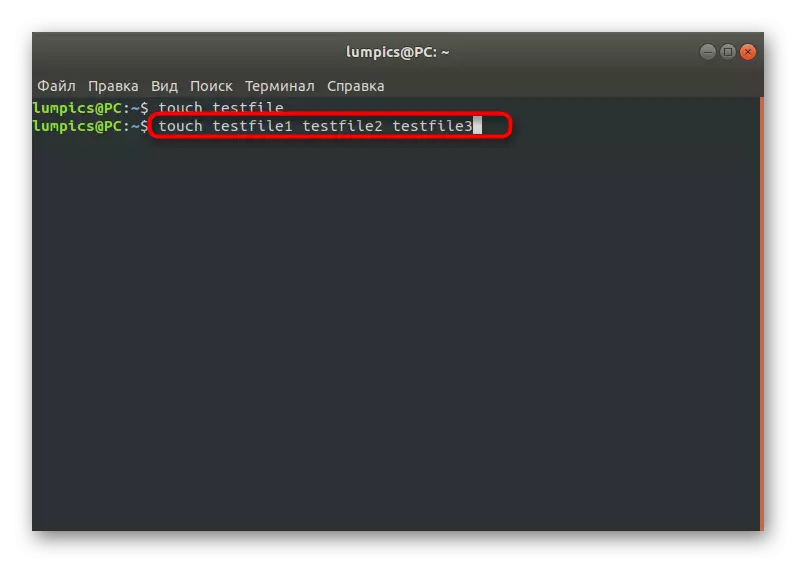
- You can add multiple files at the same time, in turn, by writing the name of everyone so that it turns out something like this line: Touch TestFile1 TestFile2 TestFile3.
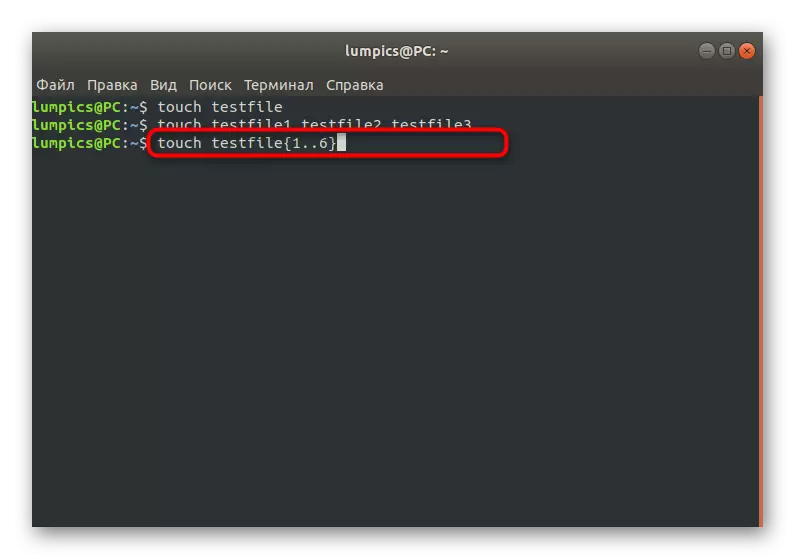
- There is one feature that should also be considered. If you have a need to create multiple files with the same name, but with different numbers at the end, as shown above, it is easier to use this type of writing: Touch TestFile {1..6}.

More Touch command without applying arguments is not able to do anything, so let's immediately proceed to the analysis of examples of interaction with options.
Setting the last access time
As you already know, one of the options under consideration allows you to change the access to the current to the current. This is done by entering only one line that has the type of touch -a file, where File is the name of the required object. The number of listed items for one line is not limited. At the same time, the last change time is not set, unless an additional option -m is optional in this row, we will talk about it further.

Setting the last change time
For the same analogy, the above-mentioned argument is also operating. OE reassigns the last time time on the current, and the string looks like this: Touch -m File. All changes made come into effect immediately, which means that you can switch to their verification or to perform other tasks for which the Touch command with the -m option was called.

Ban on creating an object
A simple TOUCH utility sometimes allows you to implement and a complex goal by entering the literal one line into the console. After executing the TOUCH -C File command, where File is the exact name of the desired file, the item with the specified name cannot be created by the usual user. This option is deactivated only after the privileged user creates an empty object with the same name through the same command. Additionally, nothing prevents you from creating a list of titles to simultaneously establish limitations on them.
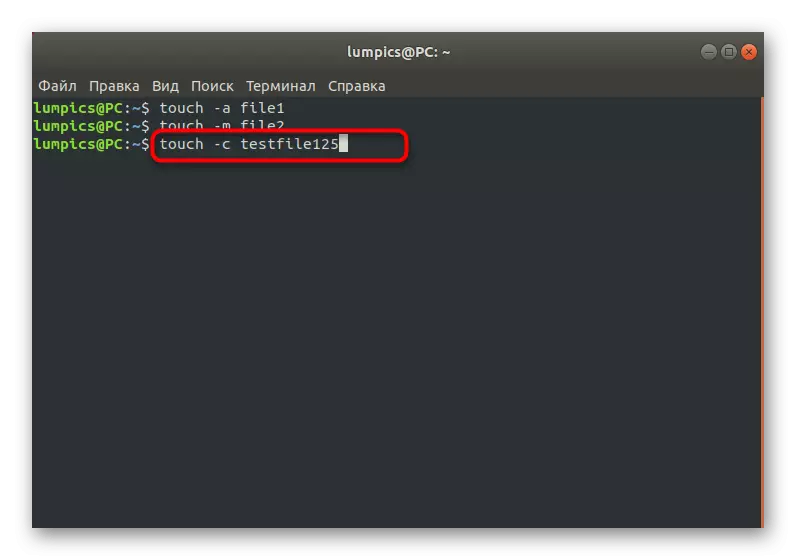
Setting the Access Time and Change
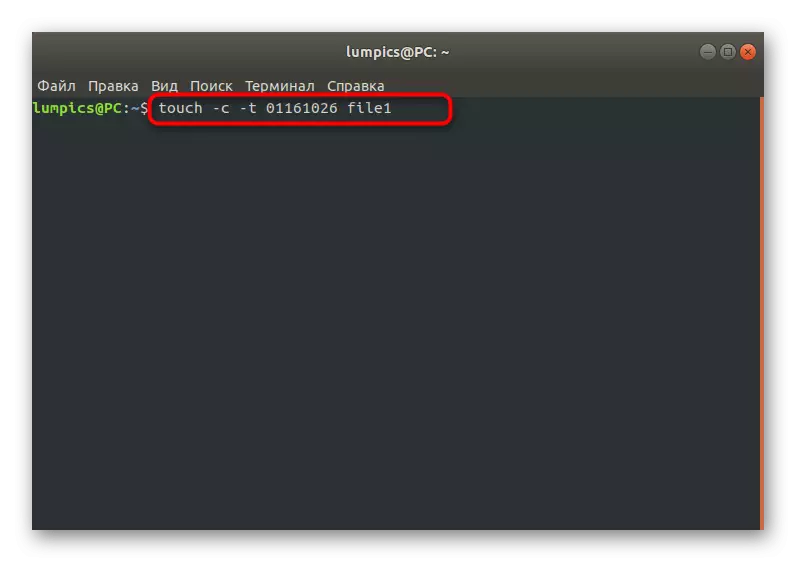
The above options -a and -M allowed only to change the file settings by setting the current time, but it is possible to set absolutely any time up to a second. At the same time, the main thing is to comply with the commissioning rule: [[BB] GG] MDDDHCHMM [.SSS], where explosives - the first two digits of the year, GG - second, mm - month, DD - date, CH - watches, mm - minutes, SS - seconds. The necessary command is obtained: Touch -C -T 01261036 File.
If you are interested in viewing the final result, write in the LS -L console and click on ENTER. The list remains only to find the desired file and view when it has been modified.

Transfer of temporary marks of the selected file
If you have familiarized yourself with the above information, you know that the -R option will be allowed to transfer temporary labels of one object to another. It is carried out through the string: Touch -R File1 File2, where File1 is an existing file with certain time marks, and File2 is a new object to which they will be applied.
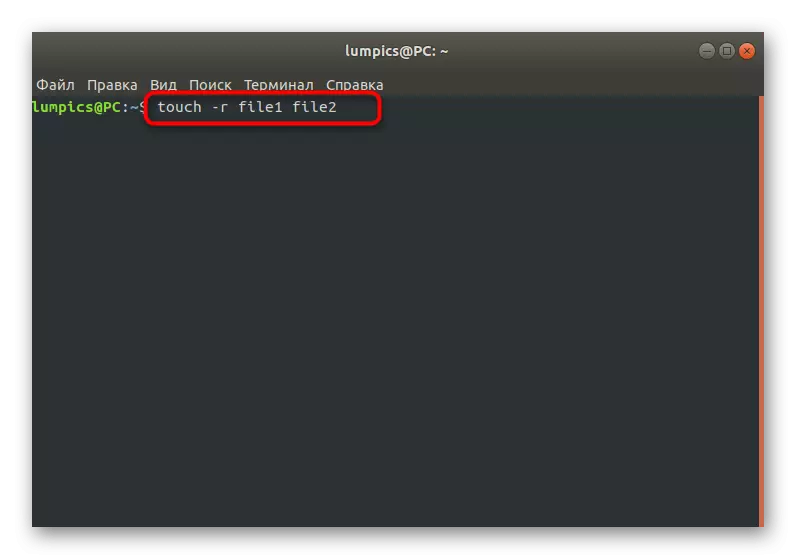
Creating a file with the specified time
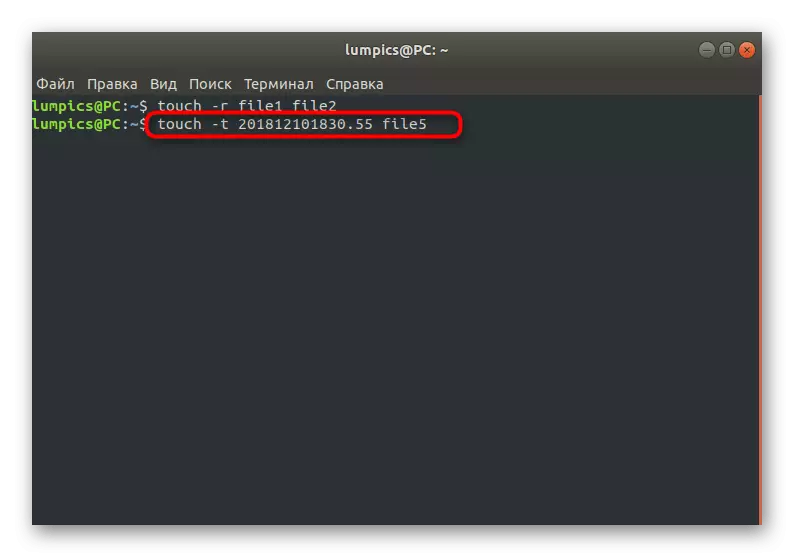
At the end of this material, we note that by default the Touch creates files up to date, however it can be changed by applying only one option: Touch -t 201912101830.55 File, where 201912101830.55 - exactly the specified time on your choice, and File is the name of the very object or objects if they are presented as a list.
Now you are familiar with the Touch command, which is actively used in Linux to create files. It can be both separate test elements and objects added for certain purposes. The user already decides itself, in which direction to apply the capabilities of the utility. If you are interested in the topic of the main teams of this operating system, we suggest to explore the following materials.
See also:
Frequently used commands in "Terminal" Linux
LN / FIND / LS / GREP / PWD command in Linux
