
Automatic creation and saving memory dumps is not always included in Windows 10, and in the instructions on the topic of fixing certain bsod errors, I have to describe and the path to turn on automatically saving memory dumps in the system for subsequent viewing in BlueScreenView and analogs - therefore was It was decided to write a separate guide to how to enable automatic creation of a memory dump during system errors to further refer to it.
Setting the creation of memory dumps when Windows 10 errors
In order to enable automatic saving system error dump file, it is enough to perform the following simple steps.
- Go to the control panel (for this in Windows 10, you can start typing "Control Panel" in the search panel in the taskbar) if "Categories" is included in the control panel in the "View" field, set the "icons" and open the "System" item.
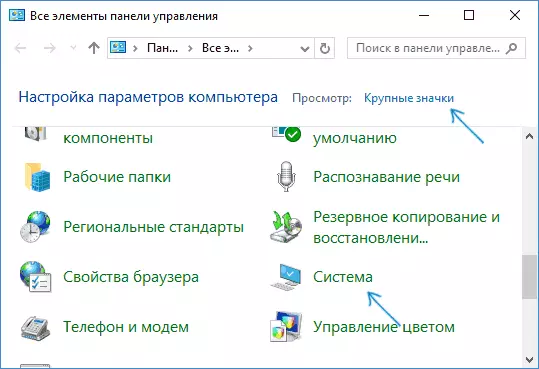
- On the left menu, select "Advanced System Parameters".

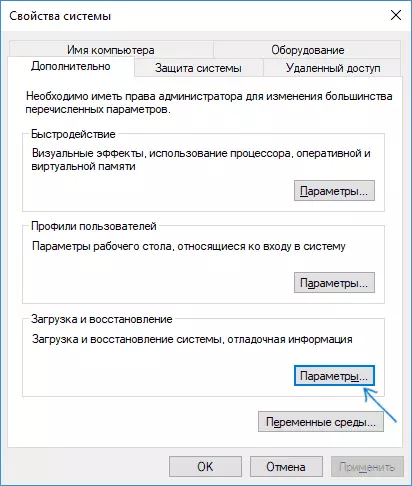
- On the Advanced tab, in the "Download and Recovery" section, click the "Parameters" button.
- The parameters for creating and saving memory dumps are in the "System Failure" section. By default, write options in the system log, automatic reloading and replacing an existing memory dump, a "automatic memory dump" is created, stored in% Systemroot% \ Memory.dmp (i.e., the MEMORY.DMP file inside the Windows system folder). Parameters To enable automatic memory creation dumps used by default, you can also see on the screenshot below.
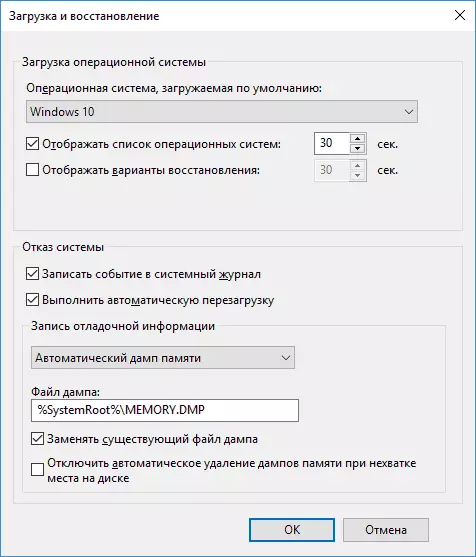
The "Automatic Memory Dump" option saves the Windows 10 kernel memory snapshot with the necessary debug information, as well as the memory allocated for devices, drivers and software operating at the kernel level. Also, when you select an automatic memory dump, small memory dumps are saved in the C: \ Windows \ miniDUMP folder. In most cases, this parameter is optimal.
In addition to the "automatic memory dump" in the preservation of debug information, there are other options:
- A full memory dump - contains a complete picture of Windows RAM. Those. The size of the Memory.dmp memory dump file will be equal to the volume of the (occupied) RAM at the time of the error appear. The usual user is usually not required.
- The kernel memory dump - contains the same data as "automatic memory dump", in fact it is the same option, except for how Windows sets the size of the paging file in case of one of them. In general, the "automatic" option is suitable (more for those interested in English - here.)
- Small memory dump - creation only mini dumps in C: \ Windows \ minidump. When this option is selected, 256 KB files are saved, containing basic information about the blue death screen, the list of downloaded drivers, processes. In most cases, with non-professional use (for example, as in the instructions on this site to correct BSOD errors in Windows 10), just a small memory dump is used. For example, when diagnosing the reasons for the blue screen of death in BlueScreenView, mini dump files are used. However, in some cases, the full (automatic) memory dump may be required - often the software support service in case of problems (presumably caused by this software) can ask for it.
Additional Information
In case you need to remove a memory dump, you can do it manually, deleting the Memory.dmp file in the Windows system folder and the files contained in the MiniDUMP folder. You can also use the Windows Cleaning Utility (press Win + R keys, enter CleanMGR and press ENTER). In "Clearing Disc", click the "Clear System Files" button, and then in the list, check the memory dump file for system errors in order to delete them (in the absence of such items it can be assumed that the memory dumps have not yet been created).
Well, and at the end of why the creation of memory dumps can be disabled (or disconnect after switching on): most often the reason are programs for cleaning the computer and optimizing the system operation, as well as software to optimize SSD operation, which can also turn off their creation.
